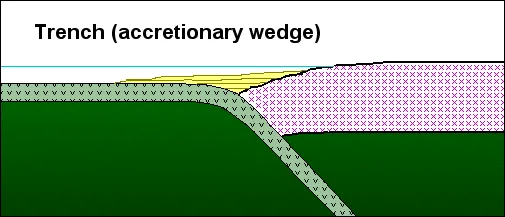
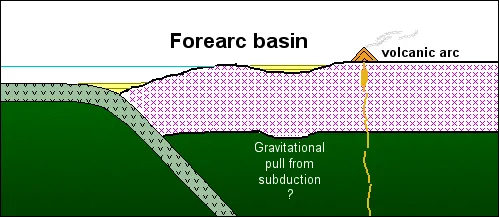
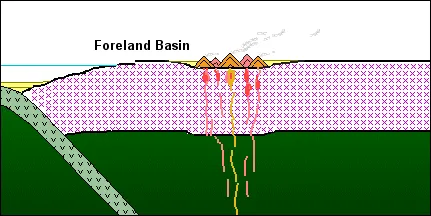
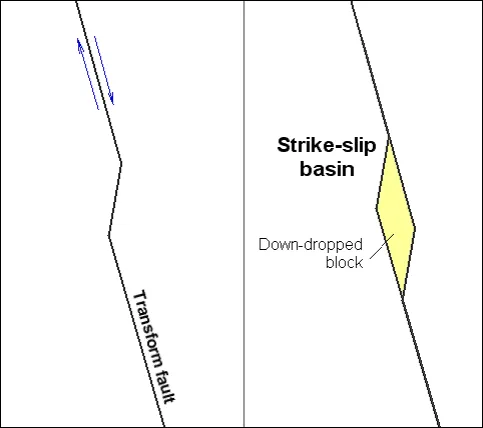
Types of sedimentary basins
Rift-related basins
Basin type
Geological Origin
Example
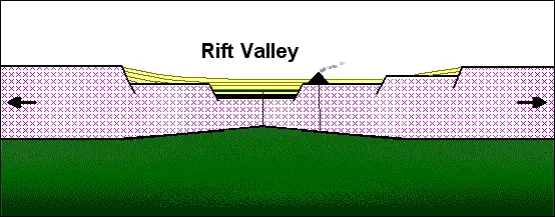
Rift basin
The down-dropped basin formed during rifting because of stretching and thinning of the continental crust
East Africa Rift
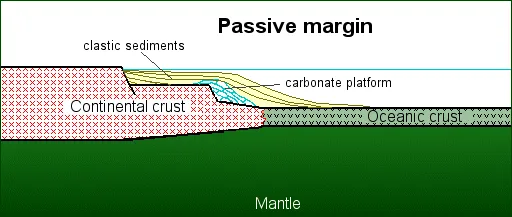
Passive margin basin
Subsidence along a passive margin, mostly due to long-term accumulation of sediments on the continental shelf
East coast of North America