Equipment Design
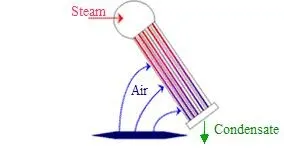
The hot vapor to be condensed travels through a series of finned copper tubes. Fans force air to circulate around the tubes, and this air removes heat from the vapor. The resulting condensate drips down the tubing into a reservoir or out a drain.
Condensers can be designed for one or two stages, as shown on the left. While the two-stage condenser is more efficient, it is also more expensive.

Usage Examples
Condensers are used in power plants to condense exhaust steam from turbines. They are also used in refrigeration plants to condense refrigeration vapors such as ammonia or fluorinated hydrocarbons. They are used in the petroleum and chemical industries to condense a variety of chemical vapors. The air cooled condensing unit shown below is a chilling system used for ice and curling rinks.

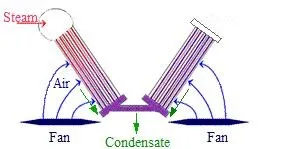
The condenser shown below has a "V-type" design that is used in refrigeration and air-conditioning installations. This condenser has aluminum fins, and the optimized V shape results in excellent heat transfer with minimized refrigerant charge.
