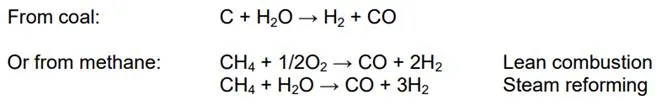
Synthesis gas (syngas)
Synthesis gas (syngas) is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. It can be created from coal or methane reacting with steam at high temperatures:
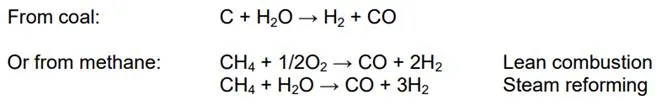
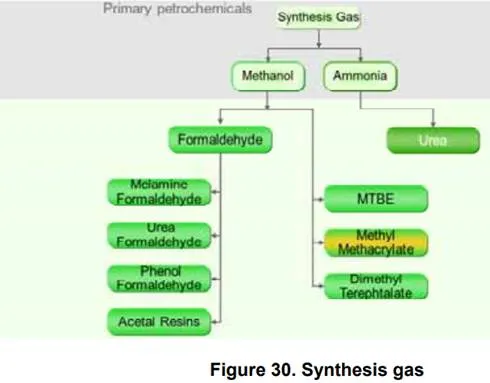
Syngas is used for production of methanol or ammonia. It is also used for production of synthetic fuels, both diesel (Fischer–Tropsch process) and gasoline.
Methanol based products Methanol, a colorless alcohol, is a chemical used in the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid and methyl methacrylate (MMA), and is used as a solvent in many applications. It is also used to produce MTBE and other products, and can be used in fuels.
Melamine resin or melamine formaldehyde (also, incorrectly, melamine) is a hard, thermosetting plastic material made from melamine and formaldehyde by polymerization. This plastic is often used in kitchen utensils or plates and is the main constituent in high pressure laminates and laminate flooring.
Urea-formaldehyde is a non-transparent thermosetting resin or plastic, made from urea and formaldehyde. It is used in adhesives, finishes, MDF and molded objects. Its attributes include high tensile strength, heat distortion temperature, low water absorption, mold shrinkage, high surface hardness and elongation at break.
Phenol formaldehyde is a low-cost basic resin. Addition of appropriate fillers can generate high temperature-resistant grades (185 °C/370 °F). Normal phenolics are resistant to 150 °C/300 °F. Applications include moldings, bottle tops, resins, chemically resistant coatings for metals, laminates, water lubricated bearings and foams for thermal insulation.
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal resin, polytrioxane, polyformaldehyde and paraformaldehyde, is an engineering plastic used to make gears, bushings and other mechanical parts. It is also known in variant trade names such as Delrin, Celcon and Hostaform. It is the most important polyacetal resin; a thermoplastic with good physical and processing properties.
Methyl methacrylate: See previous topics.
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an ester of terephthalic acid and methanol and is used in the production of polyesters, including polyethylene terephthalate and polytrimethylene terephthalate. It consists of benzene with methyl ester groups attached. DMT has largely been replaced by pure terephthalic acid (PTA) as the preferred industrial route to polyester production.
Ammonia based products
Ammonia is a pungent, colorless, gaseous alkaline compound of nitrogen and hydrogen (NH3) that is very soluble in water and can easily be condensed to a liquid by cold and pressure. It is manufactured by the direct combination of hydrogen and nitrogen under pressure over a catalyst. The main process is still the Haber-Bosch synthesis invented in 1915, operating at 15–25 MPa and between 300 and 550 °C in four reaction chambers with catalyst. Anhydrous ammonia is mainly used for the manufacture of nitrogenous fertilizers. It is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceuticals, for explosives, and is used in many commercial cleaning products.
Urea CO(NH2)2 is synthesized from ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is named for its presence in human and most land animal urine (except fish and birds). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a convenient source of nitrogen. Urea is also an important raw material for the chemical industry in animal feed, plastics and resins.