LPG Composition - What is LPG made of?
Ø The gases that fall under the “LPG” label, including ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene, normal butane, butylene, isobutane and isobutylene, as well as mixtures of these gases.
Ø The two most common are Propane and Butane.
Ø Isobutane (i-butane) is an isomer of butane with the same chemical formula as butane but different physical properties.
Ø Isobutane is converted from butane in a process called isomerization.
Ø It is classified as LPG, along with propane, butane and mixes of these gases.
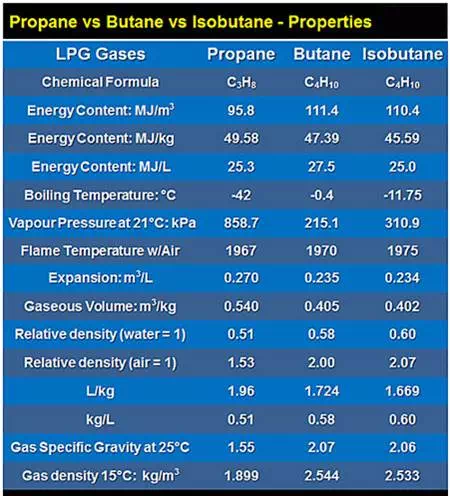
LPG Properties Chart
LPG physical properties include specific gravity (density), boiling point, pressure, vapour expansion, energy content, combustion facts, flame temperature, flash point & more.
This chart shows some of the physical properties of propane, butane and isobutane…
LPG Pressure Varies with Temperature
As previously mentioned, when LPG is stored in a gas bottle, it is under pressure.
The term “pressure” refers to the average force per unit of area that the gas exerts on the inside walls of the gas bottle.
(LPG Pressure-Temperature Chart shown)
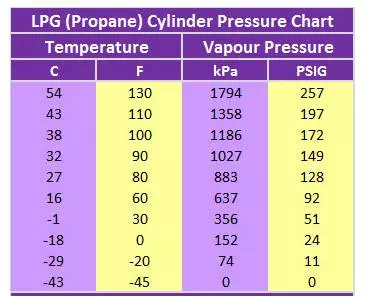
Pressure is measured in kilopascals (kPa) or pounds per square inch (psi).
LPG pressure can vary greatly based on temperature, as shown in the chart.
The level of fill in the gas bottle comes into play when the LPG is being used, as it affects the rate of vapourisation.
As LPG is a liquefied gas, the pressure inside the cylinder will remain the same from full until the last of the liquid LPG is vapourised.
Then the pressure will fall quickly as the last of the LPG vapour is used, as well.
How Much Pressure is in an LPG-Propane Cylinder?
The pressure inside of an LPG 45kg cylinder, or larger vessel, is dependent upon the temperature of the vessel.
The higher the temperature, the higher the pressure of the LPG within the cylinder.
The pressure range for LPG (propane) is from 152 kPa (24 PSIG) at 0ºC to 1794 kPa (257 PSIG) at 54ºC.
The LPG – propane – exists as both liquid and vapour (gas) within the cylinder.
The term “pressure” refers to the average force per unit of area that the gas exerts on the inside walls of the cylinder.
The pressure drops to zero at -43ºC (which is just below the boiling point for propane) and the pressure becomes greater at even higher temperatures.
LPG is Heavier Than Air

In answer to the frequently asked question "Is LPG heavier than air", the answer is "YES".
For example, if the density of air is equal to 1.00, the density of propane is 1.53.
Butane is even heavier, at 2.00. Isobutane is heavier still, at 2.07.
On the other hand, natural gas - methane - is lighter than air, at about 60% of the density of air.
Propane
In Australia, LPG is Propane.
Propane is the gas that is supplied to virtually all homes and most businesses that purchase LPG in Australia.
Propane is a flammable hydrocarbon gas with 3 carbon and 8 hydrogen atoms in a propane molecule.
The chemical formula for propane is C3H8. (Propane molecule model shown)
Propane is not made or manufactured, it is found naturally in combination with other hydrocarbons.
Propane is produced during natural gas processing and petroleum refining.
Propane processing involves the separation and collection of the gas from its petroleum base and other Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs).
Following its refinement, LPG is stored and distributed as a liquid under pressure until used, at which point it is utilised as either a liquid or a gas (vapour).
LPG is supplied in gas bottles that are either exchanged or refilled on site by LPG tankers.
Large users may utilise bigger LPG storage tanks.
Propane Combustion Formula
In the presence of sufficient oxygen, LPG burns to form water vapour and carbon dioxide, as well as heat.
Formula for Complete Combustion of LPG (propane):
Propane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Heat
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + Heat
If not enough oxygen is present for complete combustion of LPG (propane), incomplete combustion occurs with water, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide being produced.
Formula for Incomplete Combustion of LPG (propane):
Propane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Carbon Monoxide + Water + Heat
2 C3H8 + 9 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 CO + 8 H2O + heat