What is Natural Gas - Methane Gas? Types of Natural Gas (Methane & NGLs)
Ø Natural gas is primarily Methane. Methane gas color is clear and it is odourless without an odourant additive.
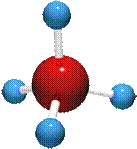
Ø When it is extracted from the ground it may also contain Ethane, Propane, Butane, and Pentane.
Ø The natural gas liquids - NGLs - are separated out for individual distribution.
Ø Most of these are usually stripped out for other specific applications before it is passed along through the pipelines.
Ø Impurities are also removed, including water and sulphur.
Ø The chemical formula for Methane is CH4.
Natural Gas - Methane - Uses
Ø Natural gas is used primarily as fuel to generate heat.
Ø In homes this includes hot water, cooking and heating.
Ø In industrial applications, it commonly heats boilers for various processes, as well as dryers, ovens and kilns.
Ø When compressed into CNG, it can also be used to fuel vehicles.
Ø The generation of electricity is also a major use of natural gas, as it is much cleaner that coal fired generation.
Ø Electricity generation can be via direct gas powered turbines, indirectly with steam turbines or a combination of the two, where the waste heat from the gas turbines is recycled to produce steam and drive steam turbines.
How Do We Get Natural Gas
Ø Natural gas is a fossil fuel.
Ø It is formed over millions of years from decayed biomass subject to heat and pressure.
Ø So, natural gas is found deep underground in various rock formations.
Ø It is accessed by drilling deep wells.
Ø The "wet" gas that comes from the well must be processed to separate out the natural gas liquids, like LPG, as well as water and other impurities.
Ø Finally, the dry gas is passed through the gas pipelines that deliver it to our homes and businesses.
Natural Gas Composition
Ø Natural gas is primarily methane.
Ø Methane molecules consist of hydrogen and carbon, with a formula of CH4.
Ø As noted previously, raw natural gas may include propane, butane, isobutane, ethane, ethene, propene, isobutene, butadiene, pentane, and pentene and pentanes plus.
Ø Impurities such as water vapour, hydrogen sulphide (H2S), carbon dioxide, helium and nitrogen are also found in raw natural gas and must be removed.
Methane Propane Butane - Is There Methane in Propane or Butane?
There is no methane in propane or butane.
Methane, butane and propane are three distinctly different gases.
Simulated Natural Gas or Synthetic Natural Gas
Ø Simulated Natural Gas – SNG – is produced by mixing vaporised LPG with compressed air.
Ø SNG can be used in place of natural gas, as it has virtually identical combustion characteristics.
Ø It can be used alone or mixed with regular natural gas.
Ø No changes are required in burners, regulators or gas jets.
Ø Simulated natural gas has a number of names.
Ø In addition to SNG, it is also called propane-air and LPG-air.
Pictured below is a simulated natural gas installation:

Images courtesy of TransTech
Under what Circumstance or Situation will LPG be added to LNG?
Ø Normally, you would never add LPG to LNG, as the combustion properties are so different..
Ø The one exception is with SNG - Synthetic Natural Gas, after the LNG returns to its gaseous state.
Ø Once the LNG has been regasified, LPG could be added to it - in the form of SNG - to increase the available supply.
Ø LPG freezes at −187.7°C (−305.8°F), meaning that there is little margin for error when chilling the methane to −161°C.
Piped Gas
Ø Natural gas or “mains gas” is the gas supplied to homes and businesses by gas pipelines or “gas mains” (reticulation systems).
Ø This is how most Australians receive their gas.
CNG Composition (Compressed Natural Gas) - Natural Gas Bottles
Ø CNG gas is distributed in natural gas bottles. A natural gas bottle is different from an LPG cylinder including much higher pressure and a lower energy content.
Ø Methane gas can be stored at high pressure, typically over 200 bars, but it is not very economical for long distance transport.
Ø CNG does have some specific applications where the product is used in close proximity to where it is compressed.
Ø City buses are a good example of a successful CNG application.
What is the Difference Between CNG & PNG?
1. The only difference between CNG and PNG is the form of delivery.
2. CNG comes out of a bottle whilst PNG comes out of a pipe.
3. Both are refined natural gas with methane being the primary constituent.
LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas)

ü Methane gas is processed into LNG by cooling it to −161°C, at which point it becomes a liquid.
ü This reduces the volume of the natural gas by a factor of more than 600 times as it goes from its gaseous state to liquid.
ü That's like going from a beach ball to a ping pong ball.
ü This reduced volume facilitates economical transport by sea or road.
ü Common LNG uses include industrial applications and long haul trucking.
ü The technology involved with LNG is generally not cost effective for small volume users, such as homes and small businesses.
ü For more information, please visit the Elgas LNG web site.