Hydropower
Hydropower is energy in moving water
Source: Adapted from National Energy Education Development Project
Source: Tennessee Valley Authority (public domain)
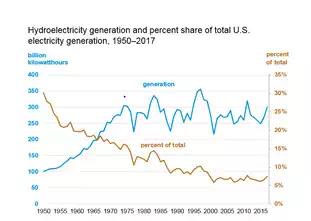
People have a long history of using the force of water flowing in streams and rivers to produce mechanical energy. Hydropower was one of the first sources of energy used for electricity generation and is the largest single renewable energy source for electricity generation in the United States. In 2017, hydroelectricity accounted for about 7.5% of total U.S. utility-scale electricity generation and 44% of total utility-scale electricity generation from renewable energy sources. Hydroelectricity’s share of total U.S. electricity generation has decreased over time, mainly because electricity generation from other sources has increased.
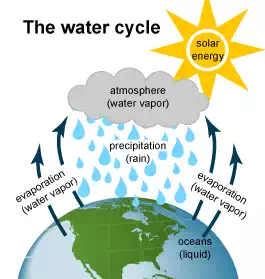
Hydropower relies on the water cycle
Understanding the water cycle is important to understanding hydropower. The water cycle has three steps:
· Solar energy heats water on the surface of rivers, lakes, and oceans, which causes the water to evaporate.
· Water vapor condenses into clouds and falls as precipitation—rain and snow.
· Precipitation collects in streams and rivers, which empty into oceans and lakes, where it evaporates and begins the cycle again.
The amount of precipitation that drains into rivers and streams in a geographic
area determines the amount of water available for producing hydropower.
Seasonal variations in precipitation and long-term changes in precipitation
patterns, such as droughts, have a big impact on hydropower production.
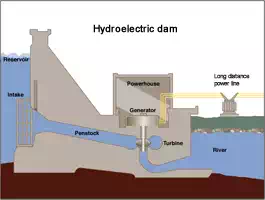
Hydroelectric power is produced from moving water
Because the source of hydroelectric power is water, hydroelectric power plants are usually located on or near a water source. The volume of the water flow and the change in elevation (or fall) from one point to another determine the amount of available energy in moving water. Swiftly flowing water in a big river, such as the Columbia River that forms the border between Oregon and Washington, carries a great deal of energy in its flow. Water descending rapidly from a high point, such as Niagara Falls in New York, also has substantial energy in its flow.
At both Niagara Falls and the Columbia River, water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies pressure on a turbine. In a storage system, water accumulates in reservoirs created by dams and is released as needed to generate electricity.
History of hydropower
Hydropower is one of the oldest sources of energy for producing mechanical and electrical energy. Hydropower was used thousands of years ago to turn paddle wheels to help grind grain. Before steam power and electricity were available in the United States, grain and lumber mills were powered directly with hydropower. The first industrial use of hydropower to generate electricity in the United States occurred in 1880, when 16 brush-arc lamps were powered using a water turbine at the Wolverine Chair Factory in Grand Rapids, Michigan. The first U.S. hydroelectric power plant opened on the Fox River near Appleton, Wisconsin, on September 30, 1882. Most of U.S. hydroelectricity is now produced at large dams on major rivers, and most of these hydroelectric dams were built before the mid-1970's.
Hydropower generators produce clean electricity, but hydropower does affect the environment
Most dams in the United States were built mainly for flood control, municipal water supply, and irrigation water. Although many of these dams have hydroelectric generators, only a small number of dams were built specifically for hydropower generation. Hydropower generators do not directly emit air pollutants. However, dams, reservoirs, and the operation of hydroelectric generators can affect the environment.
Fish ladder at the Bonneville Dam on the Columbia River separating Washington and Oregon

A dam that creates a reservoir (or a dam that diverts water to a run-of-river hydropower plant) may obstruct fish migration. A dam and reservoir can also change natural water temperatures, water chemistry, river flow characteristics, and silt loads. All of these changes can affect the ecology and the physical characteristics of the river. These changes may have negative effects on native plants and on animals in and around the river. Reservoirs may cover important natural areas, agricultural land, or archeological sites. A reservoir and the operation of the dam may also result in the relocation of people. The physical impacts of a dam and reservoir, the operation of the dam, and the use of the water can change the environment over a much larger area than the area a reservoir covers. Manufacturing the concrete and steel in hydropower dams requires equipment that may produce emissions. If fossil fuels are the energy sources for making these materials, then the emissions from the equipment could be associated with the electricity that hydropower facilities generate. However, given the long operating lifetime of a hydropower plant (50 years to 100 years) these emissions are offset by the emissions-free hydroelectricity. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane may also form in reservoirs and be emitted into the atmosphere. The exact amounts of greenhouse gases that form in hydropower reservoirs is uncertain. The greenhouse effect from the emissions from reservoirs in tropical and temperate regions, including the United States, may be equal to or greater than the greenhouse effect of the carbon dioxide emissions from an equivalent amount of electricity generation with fossil fuels. Scientists at Brazil's National Institute for Space Research designed a system to capture methane in a reservoir and burn it to produce electricity.
Fish ladders help salmon reach their spawning grounds
Hydropower turbines kill and injure some of the fish that pass through the turbine. The U.S. Department of Energy has sponsored the research and development of turbines that could reduce fish deaths to lower than 2%, in comparison with fish kills of 5% to 10% for the best existing turbines.
Many species of fish, such as salmon and shad, swim up rivers and streams from the sea to reproduce in their spawning grounds in the beds of rivers and streams. Dams can block their way. Different approaches to fixing this problem include the construction of fish ladders and elevators that help fish move around or over dams to the spawning grounds upstream.
Tidal Power
The gravitational pull of the moon and sun along with the rotation of the earth cause the tides. In some places, tides cause water levels near the shore to vary up to 40 feet. People in Europe harnessed this movement of water to operate grain mills more than a 1,000 years ago. Today, tidal energy systems generate electricity. Producing tidal energy economically requires a tidal range of at least 10 feet.
Barrage of the tidal power plant on the estuary of the Rance River in Bretagne, France

Tidal barrages
One type of tidal energy system uses a structure similar to a dam called a barrage. The barrage is installed across an inlet of an ocean bay or lagoon that forms a tidal basin. Sluice gates on the barrage control water levels and flow rates to allow the tidal basin to fill on the incoming high tides and to empty through an electricity turbine system on the outgoing ebb tide. A two-way tidal power system generates electricity from both the incoming and outgoing tides.
A potential disadvantage of tidal power is the effect a tidal station can have on plants and animals in estuaries of the tidal basin. Tidal barrages can change the tidal level in the basin and increase turbidity (the amount of matter in suspension in the water). They can also affect navigation and recreation.
Several tidal power barrages operate around the world. The Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station in South Korea has the largest electricity generation capacity at 254 Megawatts (MW). The oldest and second-largest operating tidal power plant is in La Rance, France, with 240 MW of electricity generation capacity. The next largest tidal power plant is in Annapolis Royal in Nova Scotia, Canada, with 20 MW of electricity generation capacity. China, Russia, and South Korea all have smaller tidal power plants.
The United States does not have any tidal power plants, and it only has a few sites where tidal energy could be economical to produce. France, England, Canada, and Russia have much more potential to use tidal power.
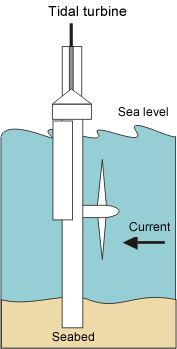
Tidal turbines
Tidal turbines look similar to wind turbines. They can be placed on the sea floor where there is strong tidal flow. Because water is about 800 times denser than air, tidal turbines have to be much sturdier and heavier than wind turbines. Tidal turbines are more expensive to build than wind turbines but capture more energy with the same size blades. The tidal turbine projects in Scotland and South Korea have tidal turbines with 1.5 MW electricity generation capacity. The project in Scotland is planning to have up to 400 MW of electricity generation capacity. A demonstration tidal turbine project is under development in the East River of New York.
Tidal fences
A tidal fence is a type of tidal power system that has vertical axis turbines mounted in a fence or row placed on the sea bed, similar to tidal turbines. Water passing through the turbines generates electricity. As of the end of 2017, no tidal fence projects were operating.
Wave Power:
Waves have a lot of energy
Pelamis wave power device off the coast of Portugal

Wave energy site
CETO underwater wave energy device

Waves form as wind blows over the surface of open water in oceans and lakes. Ocean waves contain tremendous energy. The theoretical annual energy potential of waves off the coasts of the United States is estimated to be as much as 2.64 trillion kilowatthours, or the equivalent of about 66% of U.S. electricity generation in 2017. The west coasts of the United States and Europe, and the coasts of Japan and New Zealand, have potential sites for harnessing wave energy.
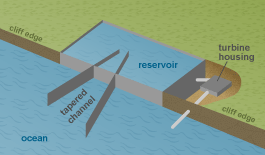
Different ways to channel the power of waves
One way to harness wave energy is to bend or focus waves into a narrow channel to increase their size and power and to spin the turbines that generate electricity. Waves can also be channeled into a catch basin or reservoir where the water flows to a turbine at a lower elevation, similar to the way a hydropower dam operates.
Many other methods of capturing wave energy are under development. These methods include placing devices on or just below the surface of the water and anchoring devices to the ocean floor. The U.S. Department of Energy's Marine and Hydrokinetic Technology Database provides information on marine and hydrokinetic renewable energy, both in the U.S. and around the world.
|
Ocean thermal energy: |
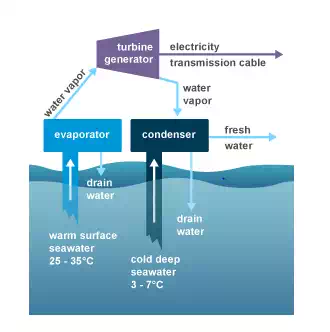
Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) is a process or technology for producing energy by harnessing the temperature differences (thermal gradients) between ocean surface waters and that of ocean depths. Energy from the sun heats the surface water of the ocean. In tropical regions, surface water can be much warmer than deep water. This temperature difference can be used to produce electricity and to desalinate ocean water. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems use a temperature difference (of at least 77o F) to power a turbine to produce electricity. Warm surface water is pumped through an evaporator containing a working fluid. The vaporized fluid drives a turbine/generator. The vaporized fluid is turned back to a liquid in a condenser cooled with cold ocean water pumped from deeper in the ocean. OTEC systems using seawater as the working fluid can use the condensed water to produce desalinated water.
The United States became involved in OTEC research in 1974 with the establishment of the Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii Authority. The laboratory is one of the world's leading test facilities for OTEC technology. The laboratory operated a 250 kilowatt (kW) demonstration OTEC plant for 6 years in the 1990s. The United States Navy supported the development of a 105 kW demonstration OTEC plant at the laboratory site. This facility became operational in 2015 and supplies electricity to the local electricity grid.
Other larger OTEC systems are in development or planned in several countries, mostly to supply electricity and desalinated water for island communities.
Ocean thermal energy conversion system
An experimental OTEC plant on the Kona Coast in Hawaii

|
|