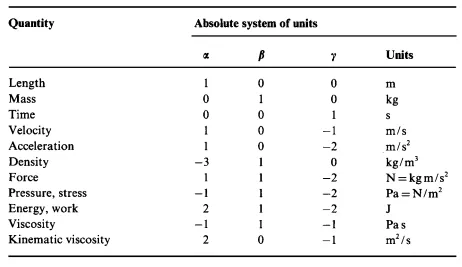
Absolute system of units
MKS system of units
This is the system of units where the metre (m) is used for the unit of length, kilogram (kg) for the unit of mass, and second (s) for the unit of time as the base units.
CGS system of units
This is the system of units where the centimetre (cm) is used for length, gram (g) for mass, and second (s) for time as the base units
International system of units (SI)
SI, the abbreviation of La Systkme International d’Unites, is the system developed from the MKS system of units. It is a consistent and reasonable system of units which makes it a rule to adopt only one unit for each of the various quantities used in such fields as science, education and industry. There are seven fundamental SI units, namely:
metre (m) for length, kilogram (kg) for mass, second (s) for time, ampere (A) for electric current, kelvin (K) for thermodynamic temperature, mole (mol) for mass quantity and candela (cd) for intensity of light. Derived units consist of these units.
