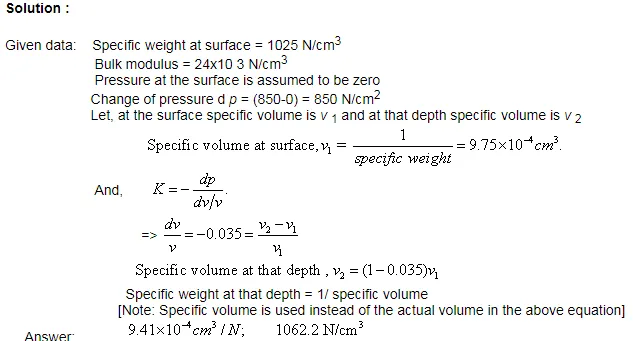System and control volume
A system refers to a fixed, identifiable quantity of mass which is separated from its surrounding by its boundaries. The boundary surface may vary with time however no mass crosses the system boundary. In fluid mechanics an infinitesimal lump of fluid is considered as a system and is referred as a fluid element or a particle. Since a fluid particle has larger dimension than the limiting volume (refer to section fluid as a continuum). The continuum concept for the flow analysis is valid.
control volume is a fixed, identifiable region in space through which fluid flows. The boundary of the control volume is called control surface. The fluid mass in a control volume may vary with time. The shape and size of the control volume may be arbitrary.
Example
A liquid is undergone a change of pressure from 6.87 MPa to 13.73 MPa to make the volumetric change of 0.0113 m3 to 0.0111 m3 . What is the bulk modulus of elasticity of the liquid?

Example
At a certain depth of a liquid where the pressure is 850 N/cm2 what will be the change in specific volume and specific weight with respect to the surface? Given that the specific weight of that liquid at the surface is 1025 N/cm3 and the bulk modulus of elasticity is 24x10 3 N/cm3 .