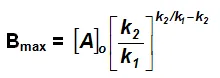Example of Sequential Reactions
· Decomposition of ethylene oxide
(CH2)2O ![]() CH3CHO
CH3CHO
CH3CHO ![]() CO + CH4
CO + CH4
· The pyrolysis of acetone
(CH3)2CO ![]() CH4 + CH2 =C=O
CH4 + CH2 =C=O
CH2 =C=O ![]() C2H4 + CO
C2H4 + CO
Consecutive or Sequential Reactions
This reaction is defined as that reaction which proceeds from reactants to final products through one or more intermediate stages. The overall reaction is a result of several successive or consecutive steps.
A → B → C and so on
Example of Sequential Reactions |
· Decomposition of ethylene oxide (CH2)2O CH3CHO · The pyrolysis of acetone (CH3)2CO CH2 =C=O |

For the reaction
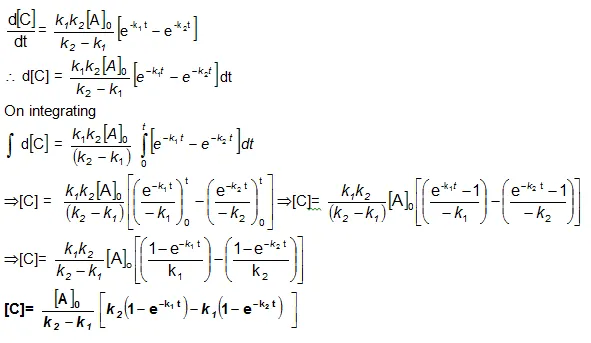
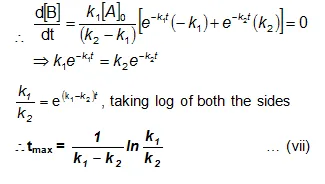 …....(i)
…....(i)
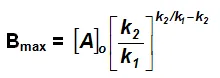 …......(ii)
…......(ii)
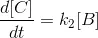 ….......(iii)
….......(iii)
Integrating equation (i), we get

Now we shall integrate equation (ii) and find the concentration of B related to time t.
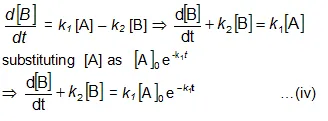
Integration of the above equation is not possible as we are not able to separate the two variables, [B] and t. Therefore we multiply equation (4) by an integrating factor ![]() , on both the sides of the equation.
, on both the sides of the equation.
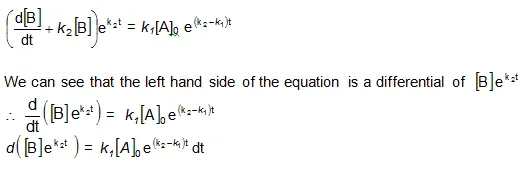
Integrating with in the limits 0 to t.
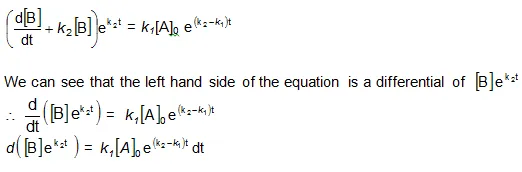
Now in order to find [C], substitute equation (vi) in equation (iii), we get
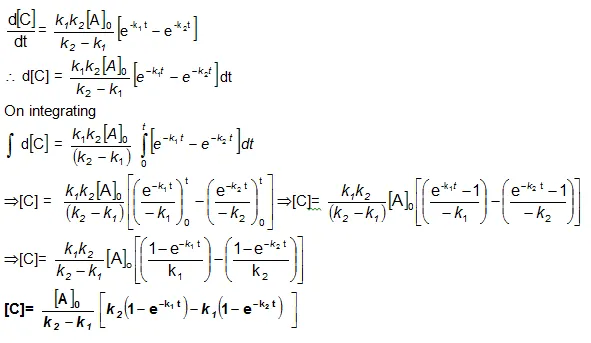
Bmax and tmax:
We can also attempt to find the time when [B] becomes maximum. For this we differentiate equation (vi) and find d[B]/dt & equate it to zero.
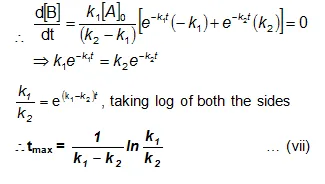
Substituting equation (vii) in equation (vi)