
Parallel and Sequential Reactions
The reactions in which a substance reacts or decomposes in more than one way are called parallel or side reactions.

If we assume that both of them are first order, we get.

k1 = fractional yield of B × kav
k2 = fractional yield of C × kav
If k1 > k2 then
A → B main and

A → C is side reaction
Let after a definite interval x mol/litre of B and y mol/litre of C are formed.

i.e
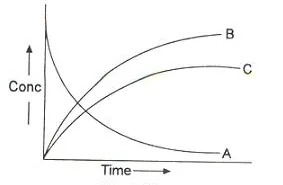
This means that irrespective of how much time is elapsed, the ratio of concentration of B to that of C from the start (assuming no B and C in the beginning ) is a constant equal to k1/k2.

Example of Parallel Reactions |
|