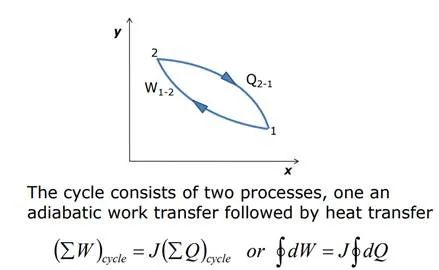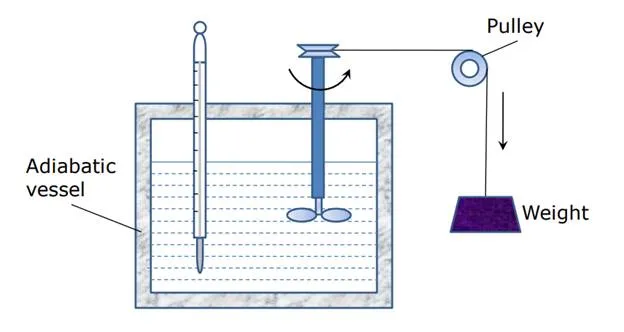
Joule’s experiment
• Joule’s experiment (1840-1849) to investigate the equivalence of heat and work.
• Prior to Joule, heat was considered to be a invisible fluid known as caloric and flows from a body of higher caloric to one with a lower caloric.
• Caloric theory of heat
• Joule’s experiment laid the foundation of the first law of thermodynamics.
Joule’s experiment

• Work, W1-2 done on the system can be measured by the fall of the weight.
• The system temperature rises as work is done on the system.
• Let the insulation now be removed.
• The system reaches its initial state by heat transfer across the system boundaries.
• Therefore the work done is proportional to the heat transfer.
• The constant of proportionality is the Joule’s equivalent.