First come first serve (FCFS) scheduling algorithm simply schedules the jobs according to their arrival time. The job which comes first in the ready queue will get the CPU first. The lesser the arrival time of the job, the sooner will the job get the CPU. FCFS scheduling may cause the problem of starvation if the burst time of the first process is the longest among all the jobs.
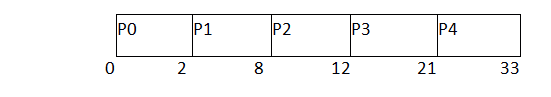
Let's take an example of The FCFS scheduling algorithm. In the Following schedule, there are 5 processes with process ID P0, P1, P2, P3 and P4. P0 arrives at time 0, P1 at time 1, P2 at time 2, P3 arrives at time 3 and Process P4 arrives at time 4 in the ready queue. The processes and their respective Arrival and Burst time are given in the following table.
The Turnaround time and the waiting time are calculated by using the following formula.
· Turn Around Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
The average waiting Time is determined by summing the respective waiting time of all the processes and divided the sum by the total number of processes.
Process ID | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Completion Time | Turn Around Time | Waiting Time |
0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 1 |
2 | 2 | 4 | 12 | 8 | 4 |
3 | 3 | 9 | 21 | 18 | 9 |
4 | 4 | 12 | 33 | 29 | 17 |
Avg Waiting Time=31/5

(Gantt chart)
FCFS may suffer from the convoy effect if the burst time of the first job is the highest among all. As in the real life, if a convoy is passing through the road then the other persons may get blocked until it passes completely. This can be simulated in the Operating System also.
If the CPU gets the processes of the higher burst time at the front end of the ready queue then the processes of lower burst time may get blocked which means they may never get the CPU if the job in the execution has a very high burst time. This is called convoy effect or starvation.
In the Example, We have 3 processes named as P1, P2 and P3. The Burt Time of process P1 is highest.
The Turnaround time and the waiting time in the following table, are calculated by the formula,
· Turn Around Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
In the First scenario, The Process P1 arrives at the first in the queue although; the burst time of the process is the highest among all. Since, the Scheduling algorithm, we are following is FCFS hence the CPU will execute the Process P1 first.
In this schedule, the average waiting time of the system will be very high. That is because of the convoy effect. The other processes P2, P3 have to wait for their turn for 40 units of time although their burst time is very low. This schedule suffers from starvation.
Process ID | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Completion Time | Turn Around Time | Waiting Time |
1 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 0 |
2 | 1 | 3 | 43 | 42 | 39 |
3 | 1 | 1 | 44 | 43 | 42 |
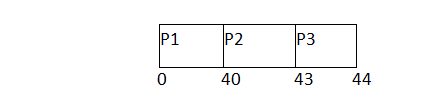
Avg waiting Time = 81/3
In the Second scenario, If Process P1 would have arrived at the last of the queue and the other processes P2 and P3 at earlier then the problem of starvation would not be there.
Following example shows the deviation in the waiting times of both the scenarios. Although the length of the schedule is same that is 44 units but the waiting time will be lesser in this schedule.
Process ID | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Completion Time | Turn Around Time | Waiting Time |
1 | 1 | 40 | 44 | 43 | 3 |
2 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
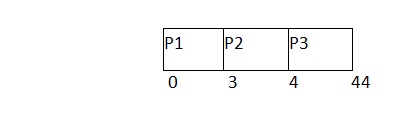
Avg Waiting Time=6/3