In the uniprograming systems like MS DOS, when a process waits for any I/O operation to be done, the CPU remains idol. This is an overhead since it wastes the time and causes the problem of starvation. However, In Multiprogramming systems, the CPU doesn't remain idle during the waiting time of the Process and it starts executing other processes. Operating System has to define which process the CPU will be given.
In Multiprogramming systems, the Operating system schedules the processes on the CPU to have the maximum utilization of it and this procedure is called CPU scheduling. The Operating System uses various scheduling algorithm to schedule the processes.
This is a task of the short term scheduler to schedule the CPU for the number of processes present in the Job Pool. Whenever the running process requests some IO operation then the short term scheduler saves the current context of the process (also called PCB) and changes its state from running to waiting. During the time, process is in waiting state; the Short term scheduler picks another process from the ready queue and assigns the CPU to this process. This procedure is called context switching.
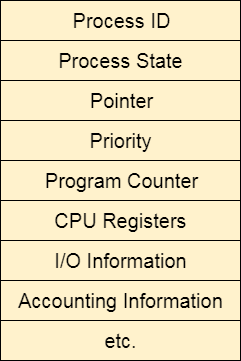
The Operating system maintains a process control block during the lifetime of the process. The Process control block is deleted when the process is terminated or killed. There is the following information which is saved in the process control block and is changing with the state of the process.

In Multiprogramming, if the long term scheduler picks more I/O bound processes then most of the time, the CPU remains idol. The task of Operating system is to optimize the utilization of resources.
If most of the running processes change their state from running to waiting then there may always be a possibility of deadlock in the system. Hence to reduce this overhead, the OS needs to schedule the jobs to get the optimal utilization of CPU and to avoid the possibility to deadlock.
There are various algorithms which are used by the Operating System to schedule the processes on the processor in an efficient way.
There are the following algorithms which can be used to schedule the jobs.
It is the simplest algorithm to implement. The process with the minimal arrival time will get the CPU first. The lesser the arrival time, the sooner will the process gets the CPU. It is the non-preemptive type of scheduling.
In the Round Robin scheduling algorithm, the OS defines a time quantum (slice). All the processes will get executed in the cyclic way. Each of the process will get the CPU for a small amount of time (called time quantum) and then get back to the ready queue to wait for its next turn. It is a preemptive type of scheduling.
The job with the shortest burst time will get the CPU first. The lesser the burst time, the sooner will the process get the CPU. It is the non-preemptive type of scheduling.
It is the preemptive form of SJF. In this algorithm, the OS schedules the Job according to the remaining time of the execution.
In this algorithm, the priority will be assigned to each of the processes. The higher the priority, the sooner will the process get the CPU. If the priority of the two processes is same then they will be scheduled according to their arrival time.
In this scheduling Algorithm, the process with highest response ratio will be scheduled next. This reduces the starvation in the system.