Need for Paging
Disadvantage of Dynamic Partitioning
The main disadvantage of Dynamic Partitioning is External fragmentation. Although, this can be removed by Compaction but as we have discussed earlier, the compaction makes the system inefficient.
We need to find out a mechanism which can load the processes in the partitions in a more optimal way. Let us discuss a dynamic and flexible mechanism called paging.
Need for Paging
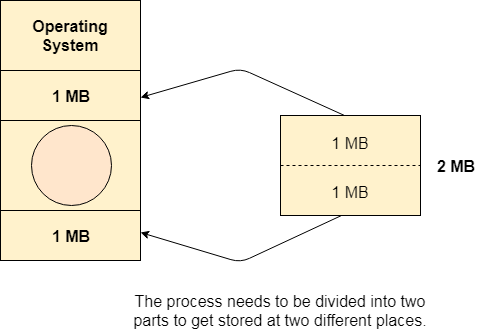
Lets consider a process P1 of size 2 MB and the main memory which is divided into three partitions. Out of the three partitions, two partitions are holes of size 1 MB each.
P1 needs 2 MB space in the main memory to be loaded. We have two holes of 1 MB each but they are not contiguous.
Although, there is 2 MB space available in the main memory in the form of those holes but that remains useless until it become contiguous. This is a serious problem to address.
We need to have some kind of mechanism which can store one process at different locations of the memory.
The Idea behind paging is to divide the process in pages so that, we can store them in the memory at different holes. We will discuss paging with the examples in the next sections.

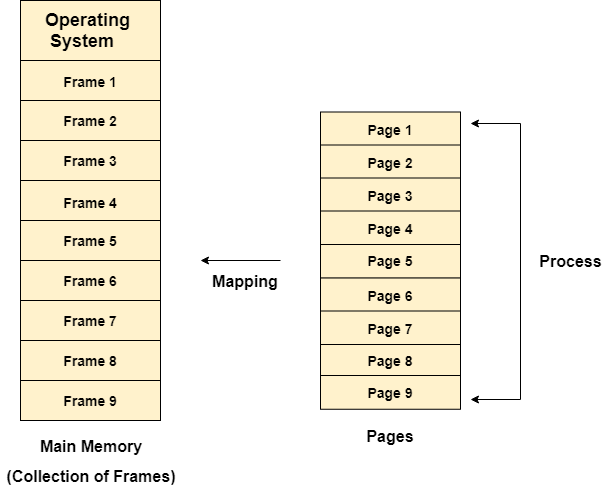
In Operating Systems, Paging is a storage mechanism used to retrieve processes from the secondary storage into the main memory in the form of pages.
The main idea behind the paging is to divide each process in the form of pages. The main memory will also be divided in the form of frames.
One page of the process is to be stored in one of the frames of the memory. The pages can be stored at the different locations of the memory but the priority is always to find the contiguous frames or holes.
Pages of the process are brought into the main memory only when they are required otherwise they reside in the secondary storage.
Different operating system defines different frame sizes. The sizes of each frame must be equal. Considering the fact that the pages are mapped to the frames in Paging, page size needs to be as same as frame size.
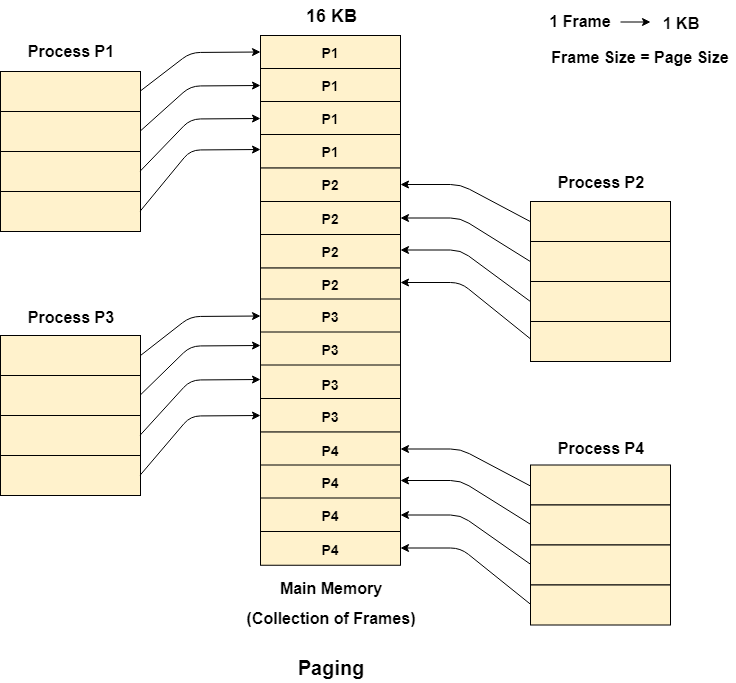
Let us consider the main memory size 16 Kb and Frame size is 1 KB therefore the main memory will be divided into the collection of 16 frames of 1 KB each.
There are 4 processes in the system that is P1, P2, P3 and P4 of 4 KB each. Each process is divided into pages of 1 KB each so that one page can be stored in one frame.
Initially, all the frames are empty therefore pages of the processes will get stored in the contiguous way.
Frames, pages and the mapping between the two is shown in the image below.
Let us consider that, P2 and P4 are moved to waiting state after some time. Now, 8 frames become empty and therefore other pages can be loaded in that empty place. The process P5 of size 8 KB (8 pages) is waiting inside the ready queue.
Given the fact that, we have 8 non contiguous frames available in the memory and paging provides the flexibility of storing the process at the different places. Therefore, we can load the pages of process P5 in the place of P2 and P4.

The purpose of Memory Management Unit (MMU) is to convert the logical address into the physical address. The logical address is the address generated by the CPU for every page while the physical address is the actual address of the frame where each page will be stored.
When a page is to be accessed by the CPU by using the logical address, the operating system needs to obtain the physical address to access that page physically.
The logical address has two parts.
Page Number
Offset
Memory management unit of OS needs to convert the page number to the frame number.