
In Priority scheduling, there is a priority number assigned to each process. In some systems, the lower the number, the higher the priority. While, in the others, the higher the number, the higher will be the priority. The Process with the higher priority among the available processes is given the CPU. There are two types of priority scheduling algorithm exists. One is Preemptive priority scheduling while the other is Non Preemptive Priority scheduling.

The priority number assigned to each of the process may or may not vary. If the priority number doesn't change itself throughout the process, it is called static priority, while if it keeps changing itself at the regular intervals, it is called dynamic priority.

In the Non-Preemptive Priority scheduling, The Processes are scheduled according to the priority number assigned to them. Once the process gets scheduled, it will run till the completion. Generally, the lower the priority number, the higher is the priority of the process. The people might get confused with the priority numbers, hence in the GATE, there clearly mention which one is the highest priority and which one is the lowest one.
In the Example, there are 7 processes P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6 and P7. Their priorities, Arrival Time and burst time are given in the table.
Process ID | Priority | Arrival Time | Burst Time |
1 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
3 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
4 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
5 | 7 | 6 | 9 |
6 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
7 | 10 | 7 | 10 |
We can prepare the Gantt chart according to the Non-Preemptive priority scheduling.
The Process P1 arrives at time 0 with the burst time of 3 units and the priority number 2. Since No other process has arrived till now hence the OS will schedule it immediately.
Meanwhile the execution of P1, two more Processes P2 and P3 are arrived. Since the priority of P3 is 3 hence the CPU will execute P3 over P2.
Meanwhile the execution of P3, All the processes get available in the ready queue. The Process with the lowest priority number will be given the priority. Since P6 has priority number assigned as 4 hence it will be executed just after P3.
After P6, P4 has the least priority number among the available processes; it will get executed for the whole burst time.
Since all the jobs are available in the ready queue hence All the Jobs will get executed according to their priorities. If two jobs have similar priority number assigned to them, the one with the least arrival time will be executed.
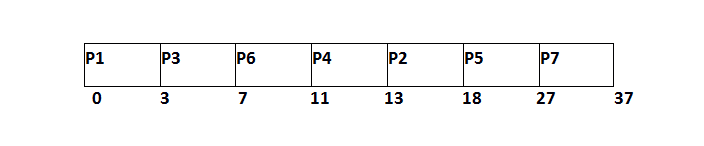
From the GANTT Chart prepared, we can determine the completion time of every process. The turnaround time, waiting time and response time will be determined.
Turn Around Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
Waiting Time = Turn Around Time - Burst Time
Process Id | Priority | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Completion Time | Turnaround Time | Waiting Time | Response Time |
1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 18 | 16 | 11 | 13 |
3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 13 | 9 | 7 | 11 |
5 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 27 | 21 | 12 | 18 |
6 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 7 |
7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 37 | 30 | 18 | 27 |
Avg Waiting Time = (0+11+2+7+12+2+18)/7 = 52/7 units