Multiplexing techniques
In fiber optic communication, multiplexing is considered to be the principal means for the expansion of existing fiber network engineering. Since optical data can be carried by employing different physical dimensions, such as time, frequency, space, polarity, etc., different multiplexing techniques are possible to be used in increasing the data-carrying capacity of a single optical fiber. This article will discuss two major multiplexing techniques currently in use—wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and optical time-division multiplexing (OTDM), and the potential techniques that are not widely used—space division multiplexing (SDM) and subcarrier division multiplexing.
Current Multiplexing Techniques in Use
Currently, multiplexing technologies have used many dimensions to increase optical transmission system capacity over a fixed bandwidth. Two major methods are WDM and OTDM. In Optical Wavelength Bands Evolution, the two high-performance methods are covered to represent the evolution of optical wavelength bands.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
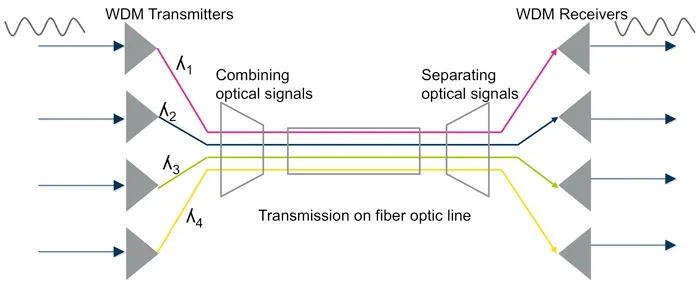
WDM is one of the optical multiplexing techniques that increases bandwidth by multiplexing a variety of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths. Each signal at WDM wavelengths is independent of any protocol and any speed. The WDM technology allows bidirectional communications simultaneously over a single optical fiber. The foundation of WDM simplifies the network to a single virtual optical fiber network instead of using multiple forms of signals with different fibers and services. In this way, WDM increases the bandwidth and lowers the networking cost by reducing the needed fibers. There are two different wavelength patterns of WDM systems, coarse (CWDM) and dense (DWDM). CWDM and DWDM are based on the same concept of using multiple light wavelengths on a single fiber, but differ in the spacing of the wavelengths, numbers of channels, and the ability to amplify the multiplexed signals in the optical space. In a WDM system, different optical signals are combined (multiplexed) together at one end of the optical fiber and separated (demultiplexed) into different channels at the other end.

The optical carrier WDM is often regarded as an analogous technique of frequency division multiplexing, which typically applies to a radio carrier. However, there is no essential difference between them since they communicate the same information.
Optical Time Division Multiplexing
OTDM is a multiplexing technique that basically multiplexes a number of low bit rate optical channels in time domain. Several low-speed optical channels are multiplexed into a fixed electrical clock period, thus increasing the transmission speed. Each signal is transmitted over a single communication channel by dividing the time frame into slots — one slot for each message signal. Based on the time, each low-speed channel is allocated to a specific position, where it works in synchronized mode. That is to say, the multiplexer and demultiplexer are timely synchronized and simultaneously switched to the next channel.

Usually, the optical pulse width is shortened in order to multiplex more channels within the fixed clock period. In addition, the shortened pulse width can reduce the crosstalk between channels because of more room left in bit rate. However, short pulse width results in heavy dispersion as traveling distance increases. Therefore, transform-limited pulse and dispersion slope compensation technique need to be used to reduce the dispersion effect on OTDM.
Potential Multiplexing Techniques in Future
Though the two multiplexing techniques above have been used in optical communication to optimize the performance of the optical fiber, there are still limitations of current technologies and with continuously increasing data demand, new multiplexing techniques are needed.
Space Division Multiplexing
SDM is a technology that utilizes the spatial dimension to simultaneously deliver different data streams by creating parallel spatial channels. This technology is commonly used in multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system. MIMO incorporates at least two antennas at the transmitter side and at least two antennas at the receiver side. And MIMO signal processing is already widely used in current coherent optical transmission systems with polarization division multiplexing (PDM) over standard single-mode fibers. It is believed that by adopting strategies using multi-core and mutil-mode fibers, long-haul transmission distance and high-speed data rates with high-density SDM are possible to achieve.
Conclusion
Among all the multiplexing technologies, WDM is the most widely used in optical communication. As different multiplexing techniques have their limitations in some aspects, it is usually suggested to use more than one technique in fiber optic networks to get the best transmission performance.