Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM)
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts together -- multiplexes -- data signals from different sources so they can share a single optical fiber pairwhile maintaining complete separation of the data streams. Each signal is carried on a separate light wavelength; the dense part of DWDM refers to the fact that more than 80 separate wavelengths, each about 0.8 of a nanometer (nm) wide, can share a single optical fiber.
DWDM allows enormous amounts of data to traverse a single network link. Because they are carried on distinct wavelengths, the streams -- also called channels -- do not interfere with each other. Consequently, data integrity is maintained, as well as any security-related partitioning -- separate tenants in the same data center, for example.
Because of its ability to handle so much data, DWDM is popular with telecommunications and cable companies and is an integral part of their core networks. It is also of interest to anyone running densely populated data centers, particularly hyperscale cloud service providers for their IaaS infrastructures or colocation providers for their densely multi-tenanted spaces, for example.
How DWDM works
DWDM wavelength channels are implemented via an array of infrared (IR) laser beams. In a system in which each channel carries 100 Gbpsand 192 channels per fiber pair, that translates to 19.2 Tbps capacity per pair. Because the channels are physically distinct and don't interfere with each other thanks to the properties of light, each of the channels can use different data formats and be transmitted at different data rates.
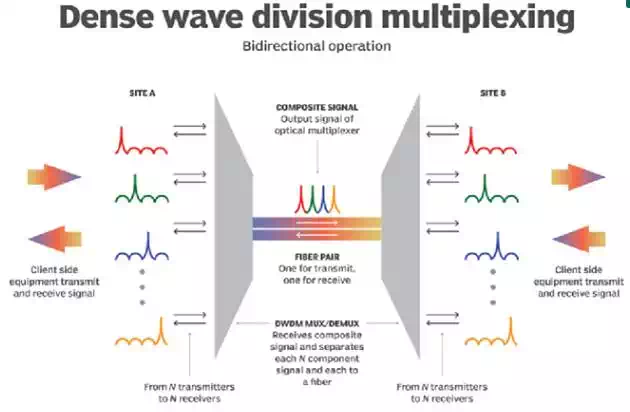
For example, IP over DWDM would permit 100 Mbps and 10 Gbps data channels to share an optical fiber, in addition to sharing it with an OC-192 Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) data channel.
Alternative to DWDM
Coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) also uses laser beams to transmit information over fiber optic cables. Because it uses less-sophisticated electronics and photonics, CWDM channels are much wider than DWDM channels, which means it supports fewer channels.