Protocols
· Define the rules that govern the communications between two computers connected to the network.
· Roles: addressing and routing of messages, error detection and recovery, sequence and flow controls etc.
· A protocol specification consists of the syntax, which defines the kinds and formats of the messages exchanged, and the semantic, which specifies the action taken by each entity when specific events occur.
Example: HTTP protocol for communication between web browsers and servers.
Request For Comments (RFC): specifications of the protocols involved in Internet Communications.
Example: sample of RFC 821 describing communications between SMTP server and client.

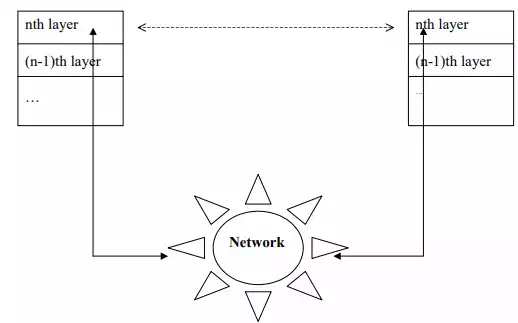
· Protocols are designed based on a layered architecture such as the OSI reference model.
· Each entity at a layer n communicates only with entities at layer n-1.
· The data exchanged, known as Protocol Data Unit (PDU), goes back and forth through the layers, each layer adds or removes its own header and vice-versa. Therefore a layer n PDU may become a layer n-1 data.