Ultrasonic C-Scan Imaging for Evaluating the Integrity of Brazed Parts
Ultrasonic Testing and C-Scan imaging represents a powerful NDT
technique for testing the integrity of metallic brazed parts. Metal-to-metal
brazing solutions are found in key sectors such as the aerospace, automotive
and nuclear industries, where high quality components are manufactured with
increased strength, fatigue tolerance, corrosion and oxidation resistance.
Brazing is a well-known method for bonding two metallic parts. As opposed to
welding where metals are melted to create a bond, brazing is done by melting a
filler metal into the metal-to-metal joint . Once liquefied, the filler metal
wets the surface and flows into the designed tight gap between the parts by
capillary action, creating a strong bond between the parts.
The integrity of the brazed joint depends on the proper wetting of the gap
created by the filler metal. In brazed joints, void defects can be formed in
the bonded area due to lack of brazing or incomplete wetting which can lead to
early component failure and poor performance.
Ultrasonic C-Scan for Braze Bond Testing
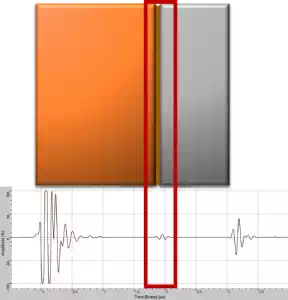
Voids in the bond area can be detected by monitoring the ultrasonic echoes reflected from the bond between the two materials. When performing ultrasonic pulse-echo testing on a brazed part, the amplitude of the echo provides the indications from the voids while the C-Scan shows the voids sizes and total area, thus revealing the overall bond quality.
Weak echo (low amplitude):
A good bonding in the brazed area results will provide Weak echo since the
ultrasounds can easily transmit from one material to another.
Typical Echo from good bonded brazed joint
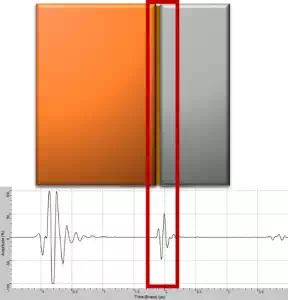
Strong echo (high amplitude):
A lack of mechanical bonding in the brazed area results, will provide strong echoes
from the interface of the brazed area. The echoes represent reflections from
voids created due to lack of brazing.
A Typical Echo from bad bonded brazed joint
To perform complete inspection of a brazed joint for aerospace components or industrial parts: automated, immersion ultrasonic testing is used, providing C-Scan images and accurate bond quality evaluation.
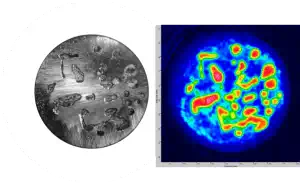
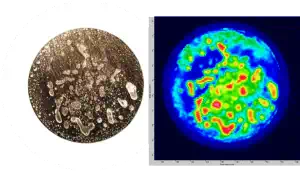
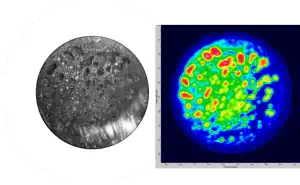
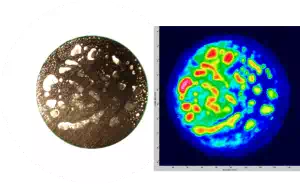
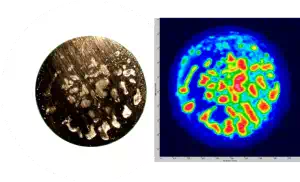
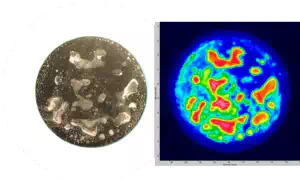
Brazed Silver-Copper Electrical Switching Contacts
A series of silver-copper samples presenting voids in the metal-to-metal brazing was inspected using immersion ultrasonic testing and compared to a metallurgical analysis, performed after precision ground (smoothing of the surface) to reveal the voids. As a reference, the diameter of the parts is approximately 15 mm.
Comparison of metallurgical analysis and corresponding C-Scan images of voids within a silver-copper brazed joint