MySQL View
In MySQL, View is a virtual table created by a query by joining one or more tables.
MySQL Create VIEW
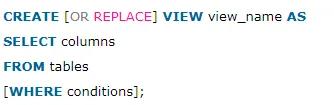
A VIEW is created by SELECT statements. SELECT statements are used to take data from the source table to make a VIEW.
Syntax:
Parameters:
OR REPLACE: It is optional. It is used when a VIEW already exist. If you do not specify this clause and the VIEW already exists, the CREATE VIEW statement will return an error.
view_name: It specifies the name of the VIEW that you want to create in MySQL.
WHERE conditions: It is also optional. It specifies the conditions that must be met for the records to be included in the VIEW.
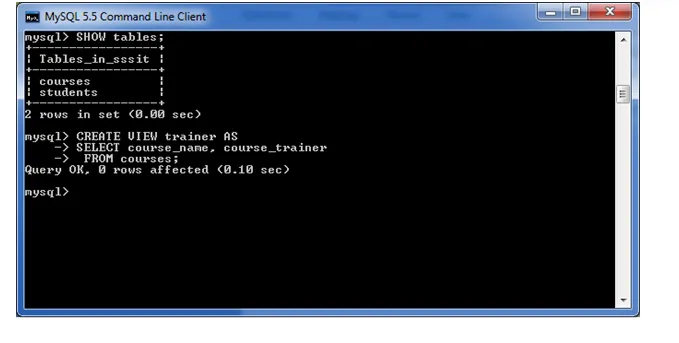
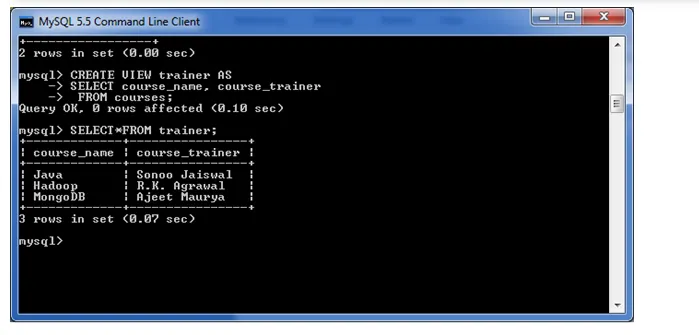
The following example will create a VIEW name "trainer". This is a virtual table made by taking data from the table "courses".
CREATE VIEW trainer AS
SELECT course_name, course_trainer
FROM courses;

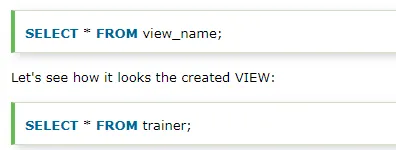
To see the created VIEW:
Syntax:

MySQL Update VIEW
In MYSQL, the ALTER VIEW statement is used to modify or update the already created VIEW without dropping it.
Syntax:
ALTER VIEW view_name AS
SELECT columns
FROM table
WHERE conditions;
Example:
The following example will alter the already created VIEW name "trainer" by adding a new column.
ALTER VIEW trainer AS
SELECT course_name, course_trainer, course_id
FROM courses;

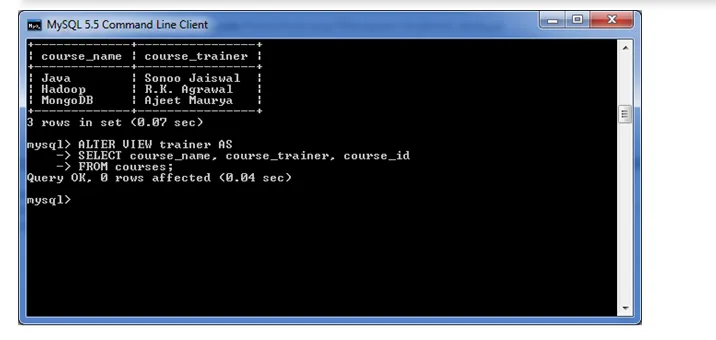
To see the altered VIEW:
SELECT*FROM trainer;


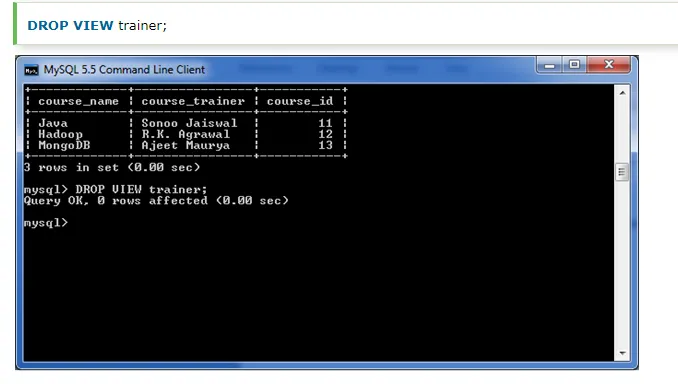
MySQL Drop VIEW
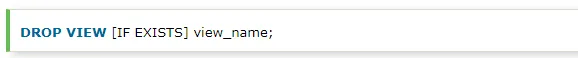
You can drop the VIEW by using the DROP VIEW statement.
Syntax:
Parameters:
view_name: It specifies the name of the VIEW that you want to drop.
IF EXISTS: It is optional. If you do not specify this clause and the VIEW doesn't exist, the DROP VIEW statement will return an error.
Example: