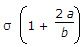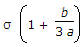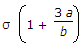15.
According to I.B.R., shearing resistance required to shear off the rivet per pitch length (in double shear) is (where n = Number of rivets per pitch length)
A. |
|
B. | 1.875 x |
C. | 2 x |
D. | 3 x |
Answer: Option B
16.
A locking device in which the bottom cylindrical portion is recessed to receive the tip of the locking set screw, is called
A. | castle nut |
B. | jam nut |
C. | ring nut |
D. | sawn nut |
Answer: Option C