Leadership Styles in Managerial Grid
Developed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton, this approach as shown in the following grid, has two dimensions:
Concern for people which includes such elements as provision of good working conditions, placement of responsibility on the basis of trust rather than concern for production.
Concern for production includes the attitudes of a supervisor toward a wide variety of things, such as quality of staff services, work efficiency, volume and quality of output, etc.
The bi-dimensional managerial grid identifies a range of management behavior based on the various ways that task-oriented and employee-oriented styles (each expressed as a continuum on a scale of 1 to 9) can interact with each other.
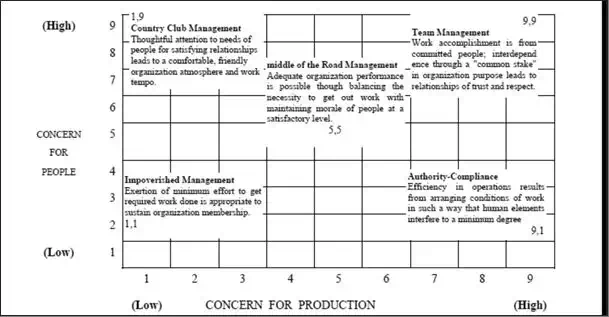
Management Style 1,1:
- Impoverished management with low concern for both people and production.
- This is called laissez-faire management because the leader does not take a leadership role.
- Also known as delegative leadership is a type of leadership style in which leaders are hands-off and allow group members to make the decisions.
Management Style 1,9:
- Country club management having high concern for employees but low concern for production.
- These leaders predominantly use reward power to maintain discipline and to encourage the team to accomplish its goals.
Management Style 5,5:
- Middle of the road management with medium concern for production and for people.
- Leaders who use this style settle for average performance and often believe that this is the most anyone can expect.
Management Style 9,1:
- Authoritarian management with high concern for production but low concern for employees exercising disciplinary pressure.
- This approach may result in high production but low people satisfaction levels.
Management Style 9,9:
- Democratic management with high concern for both production, and employee morale and satisfaction.
- The leader's high interest in the needs and feelings of employees affects productivity positively.
This theory concluded that style 9,9 is the most effective management style as this leadership approach will, in almost all situations, result in improved performance, low turnover and absenteeism, and high employee satisfaction.