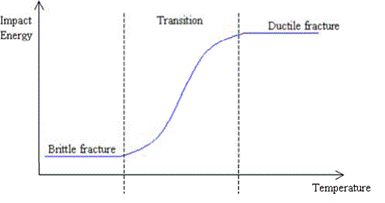
Ductile brittle transition
Ductile to brittle transition occurs in materials when the temperature is dropped below a transition temperature. Alloying usually increases the ductile-brittle transition temperature, for ceramics, this type of transition occurs at much higher temperatures than for metals.
The notched-bar impact test can be used to determine whether or not a material experiences a ductile-to-brittle transition as the temperature is decreased. In such a transition, at higher temperatures the impact energy is relatively large since the fracture is ductile. As the temperature is lowered,the impact energy drops over a narrow temperature range as the fracture becomes more brittle.
The transition can also be observed from the fracture surfaces, which appear fibrous or dull for totally ductile fracture, and granular and shiny for totally brittle fracture. Over the ductile-to- brittle transition features of both types will exist.
While for pure materials the transition may occur very suddenly at a particular temperature, for many materials the transition occurs over a range of temperatures. This causes difficulties when trying to define a single transition temperature and no specific criterion has been established.
The ductile-brittle transition is exhibited in bcc metals, such as low carbon steel, which become brittle at low temperature or at very high strain rates. Fcc metals, however, generally remain ductile at low temperatures.