Semiconductor Devices
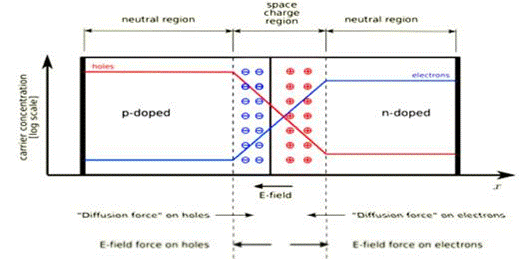
A semiconductor diode is made by the intimate junction of a p-type and an n-typesemiconductor (an n-p junction). Unlike a metal, the intensity of the electrical current that passes through the material depends on the polarity of the applied voltage. If the positive side of abattery is connected to the p-side, a situation called forward bias, a large amount of current can flow since holes and electrons are pushed into the junction region, where they recombine (annihilate). If the polarity of the voltage is flipped, the diode operates under reverse bias. Holes andelectrons are removed from the region of the junction, which therefore becomes depleted of carriers and behaves like an insulator. For this reason, the current is very small under reverse bias. The asymmetric current-voltage characteristics of diodes is used to convert alternating current into direct current. This is called rectification.
A p-n-p junction transistor contains two diodes back-to-back. The central region is very thin and is called the base. A small voltage applied to the base has a large effect on the current passing through the transistor, and this can be used to amplify electrical signals (Fig. 19.22). Anothercommon device is the MOSFET transistor where a gate serves the function of the base in a junction transistor. Control of the current through the transistor is by means of the electric field induced by the gate, which is isolated electrically by an oxide layer.