Introduction
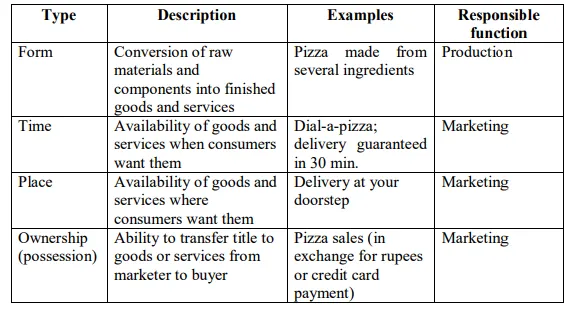
Production and marketing of goods and services are the essence of economic life in any society. All organizations perform these two basic functions to satisfy their commitments to their stakeholders – the owners, the customers and the society, at large. They create a benefit that economists call utility which is the want-satisfying power of a good or service. There are four basic kinds of utility – form, time, place and ownership utility. Form utility is created when the firm converts raw materials and component inputs into finished goods and services. Although marketing provides important inputs that specify consumer preference, the organization’s production function is responsible for the actual creation of form utility. Marketing function creates time, place and ownership utilities. Time and place utility occur when consumers find goods and services available when and where they want to purchase them. Online retailers with 24*7 format emphasize time utility. Vending machines focus on providing place utility for people buying snacks and soft drinks. The transfer of title to goods or services at the time of purchase creates ownership utility.

To survive, all organizations must create utility. Designing and marketing want satisfying goods, services and ideas is the foundation for the creation of utility. Management guru, Peter F.Drucker emphasized the importance of marketing in his classic book, The Practice of Management as:
‘If we want to know what a business is, we have start with its purpose. And its purpose must lie outside the business itself. In fact, it must lie in society since a business enterprise is an organ of society. There is one valid definition of business purpose: to create a customer’.
How does an organization create a customer? Guiltnan and Paul explain it this way:
Essentially, ‘creating’ a customer means identifying needs in the marketplace, finding out which needs the organization can profitably serve and developing an offering to convert potential buyers into customers. Marketing managers are responsible for most of the activities necessary to create the customers the organization wants, These activities include:
· Identifying customer needs
· Designing goods and services that meet those needs
· Communication information about those goods and services to prospective buyers
· Making the goods and services available at times and places that meet customers’ needs
· Pricing goods and services to reflect costs, competition and customers’ ability to buy
· Providing for the necessary service and follow-up to ensure customer satisfaction after the purchase.