Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction
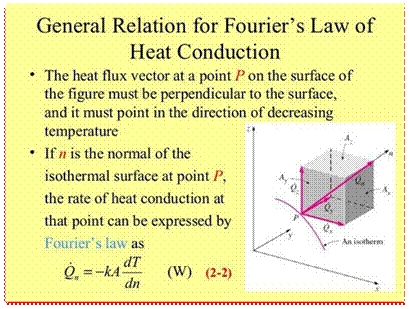
The law of heat conduction is also known as Fourier’s law. Fourier’s law states that
“the time rate of heat transfer through a material is proportional to the negative gradient in the temperature and to the area.”
Fourier’s equation of heat conduction:
Q = -kA(dT/dx)
Where,
‘Q’ is the heat flow rate by conduction (W·m−2)
‘k’ is the thermal conductivity of body material (W·m−1·K−1)
‘A’ is the cross-sectional area normal to direction of heat flow (m2) and
‘dT/dx’ is the temperature gradient (K·m−1).
§ Negative sign in Fourier’s equation indicates that the heat flow is in the direction of negative gradient temperature and that serves to make heat flow positive.
§ Thermal conductivity ‘k’ is one of the transport properties. Other are the viscosity associated with the transport of momentum, diffusion coefficient associated with the transport of mass.
§ Thermal conductivity ‘k’ provides an indication of the rate at which heat energy is transferred through a medium by conduction process.
Assumptions of Fourier equation:
§ Steady state heat conduction.
§ One directional heat flow.
§ Bounding surfaces are isothermal in character that is constant and uniform temperatures are maintained at the two faces.
§ Isotropic and homogeneous material and thermal conductivity ‘k’ is constant.
§ Constant temperature gradient and linear temperature profile.
§ No internal heat generation.
§ Fourier equation is valid for all matter solid, liquid or gas.
§ The vector expression indicating that heat flow rate is normal to an isotherm and is in the direction of decreasing temperature.
§ It cannot be derived from first principle.
§ It helps to define the transport property ‘k’.