Gas Furnace
Gas furnace is one of the oldest equipment in the heating industry. Over the years, it has evolved from the simple gas-fired-gravity heating system to the more complicated gas-fired-forced air heating system.
This type of system is used in temperate countries when heating is required to warm the houses or buildings during winter.
The common gas fuels that are used in the combustion chambers are:
● Natural Gas consists of methane and other hydrocarbons which are obtained from the gas deposits in the ground.
● Manufactured Gas is produced and consists of methane and ethane.
● Liquefied Petroleum(LP) consists of propane and butane which are pressurized to be kept in liquid state until it is ready to be used. The LP can be stored in cylinders or tanks and can be transported easily.
Gas Furnace Efficiency
The furnaces efficiency are measured using the AFUE ratings. AFUE is an acronym for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency and the higher its value, the more efficient it is. The modern equipment can have an efficiency of up to 97%.
The AFUE is measured by comparing the annual energy output to the annual energy input. If the furnace has an efficiency of 80%, it means that the piece of equipment is able to convert the 80% of fuel into useful heat energy. The balance 20% is wasted. There are three types of furnace classifications.
● Standard-Efficiency Furnace has AFUE of 78%-80% and furnace consists of draft hood, non-condensing, high flue stack temperature(up to 450°F or 232°C) and only one heat exchanger.
● Mid-Efficiency Furnace has AFUE of 78%-83% and furnace consists of forced draft, non-condensing, medium flue stack temperature(up to 300°F or 149°C) and one heat exchanger.
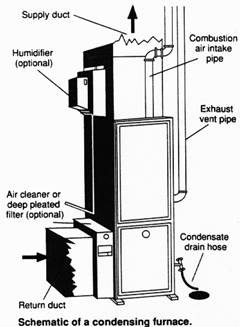
● High-Efficiency Furnace has AFUE of 87%-97% and furnace consists of forced draft, condensing, low flue stack temperature(up to 120°F or 49°C) and at least two heat exchangers. This type of furnace is also known as a condensing furnace.
Gas-Fired-Forced-Air Furnace Main Components
Control Board
The control board consists of electronic components on a printed circuit board that controls the overall operations of the gas furnace. It controls the ignition, gas valve, combustion, blower fan, draft inducer fan and safety aspects before, during and after the operations. The board will work together with a thermostat that is located in the room to regulate the air in the room.
Automatic Combination Gas Valve
This is a newer part that combines the pressure regulator and gas valve into one unit. It is used in newer furnace design and also includes the control of gas supply for the pilot and other safety features.
Burners
During the combustion of the gas in the burners, carbon dioxide, water vapor and heat will be released. The burners are made of steel or cast iron and is the place where the proper mixture of gas and air occurred.
If the combustion is not complete, carbon monoxide will be the other by-product that will be released. It is poisonous, odorless and colorless. Therefore, the installation and equipment must be tested to ensure that the combustion is as perfect as possible.
It is advisable to install a carbon monoxide detector in your house to alert you of the presence of this gas in your house.
Goodman furnace 80,000Btu
|
Combustion Blower Motor
This blower motor will exhaust the flue gases from gas furnace to the outside of the building. At the same time, it will pre-purges the heat exchanger.
Indoor Blower Motor
The indoor blower motor will cause the air to flow through the heat exchanger and into the ductwork for circulation into the space to be heated. Belt-driven or direct drive motor can be used. The more advance variable frequency drive motor is used in higher efficiency design in which the speed of the fan can be varied based on the requirements of the load.
The airflow that is optimum for the furnace to function effectively is given by the formula:
cfm=Q(s)/(1.08 X dT)
● cfm=cubic feet of air per minute
● dT=temperature difference between the return and supply air in °F
● Q(s) = sensible heat in Btu/h
Question: If a furnace has an input rating of 100,000 Btu/h, 85% efficient during stable operation and a temperature rise of 60°F. What is the cfm of the fan without taking into consideration the heat from the fan motor?
Q(s) = 100,000 X 85%= 85,000 Btu/h
cfm = 85,000/(1.08 X 60) = 1,312 cfm
Heat Exchangers
The heat exchangers are made from steel sheet which transfer the heat generated in the combustion of the gas through the steel to the air within the vicinity. These hot air is then circulated to the rooms through the ducts by using the indoor blower motor.
Air Filter
Air filter is used to filter out contaminants from the air before being circulated to the space that is being heated.

