Heat Pump Principles
There are two types of heat pumps that are commonly used today. They are known as air-to-air HP and geothermal HP. The former uses the outdoor air whereas the latter uses the underground (water or earth) temperature as its source of heating or cooling.
Using water as the source or sink gives better performance characteristics compared to the air.
Nevertheless, the air-to-air type is more economical and is popular in residential and commercial buildings applications.
These equipment work on the principle that heat will move from higher temperature to lower temperature. Therefore, a heat transfer coil that is kept a low temperature compared to its surrounding will take away the heat from the surrounding, hence cooling the space.
In order to transfer heat to the surrounding, the heat transfer device is heated up to a higher temperature than the surrounding.
This system is designed to be used for cooling the space during summer and heating during winter. The coils at the indoor and outdoor become evaporator or condenser depending on the mode of operation. If it is operating in cooling mode, the indoor coil behaves as evaporator and outdoor as condenser.
In heating mode, the indoor coil becomes a condenser and the outdoor coil evaporator. This is accomplished without moving the coils around by using a reversing valve known as four-way valve which reverses the flow of the refrigerant.
HP Operation
The HP that is commonly used is known as vapor compression refrigeration machine. An absorption machine can also be used but is not as common. The vapor compression cycle is used in our refrigerators and large industrial refrigeration systems. The diagram below shows the basic schematic of operation of a typical HP in cooling mode during summer.
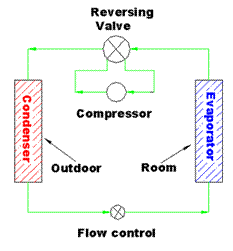
In cooling mode, the direction of the refrigerant flow is counter clockwise and the room coil is acting as an evaporator coil where the space is cooled by blowing a fan across the coil. Cool air will be generated here. The heat from the room is sink into the air, water or the ground.
During winter, heating mode is activated and the direction of the refrigerant is reversed after leaving the compressor. Take note that the flow of the refrigerant in the compressor remains the same. This reversal of flow is achieved by using a reversing valve. The air, water or ground is the source of heating.
The change of flow causes the room coil to become a condenser and the outdoor coil an evaporator. The fan that blows the room air across the condenser coil causes heat to be released into the room. The heating cycle is illustrated in the figure below.
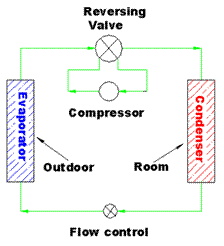
A reversing valve has four ports, two of which are opened at any one time to allow the refrigerant flow in the direction chosen.
In winter condition where temperature drops below -7°C, the heat pump heating cycle becomes less efficient as the outdoor ambient temperaure drops below freezing point. When the outdoor coil freezes with a layer of ice, the unit will have to run cooling mode to defrost the ice that accumulate on the coil.
During this time, the unit will be extracting heat from the room to the outdoor. Most controllers will stop the indoor fan from blowing the cold air into the space. This is one of the main disadvantage of this type of system when used in extreme winter condition.
Heat Pump Maintenance
Some of the actions that you can do to maintain you HP to ensure it continuous operations are listed below.
● Clean the filters, fans, indoor coils once a month or when necessary according to the recommendation of the manufacturer. Dirty filters or coils will cause the reduction of airflow in the system. The reduction of airflow will make the compressor work harder and hence more electricity is consumed.
● Clean the outdoor coils whenever they are stuck with leaves or other materials. Ensure that there is nothing near by that prevent the heat transfer to the surroundings. Do not put block the fan. Straighten fins that have been bent to ensure that the surface contact with the surrounding is good.
● Check the proper operation of the thermostat which controls the compressor, reversing valve, fans and other electronic functions.