Synchronous Motor Drives
As the name
suggests the synchronous
motors rotates
at synchronous speed. The main advantage of synchronous motors are that they
run on 3 AC supply and DC supply is given to the rotor when they run on
synchronous speed the loss is very minimal. We can say that if the synchronous
motors are designed to run only at rated synchronous speeds, then what is the use of
introducing drives to them. The answer is pretty simple,
synchronous motor drives makes the starting, pull in and braking process smooth and
without any problems. We shall discuss about them one by one.
Starting Synchronous Motors
The problem with
synchronous motors are that they are not self- starting. Before discussing the
starting method of this motor, we should know about the type of supply and the
rotor and the stator of the motor briefly.
The stator of synchronous motors are similar to that of an induction motors but the only
difference lies in the rotor, the rotor of the synchronous motors are given dc
supply.
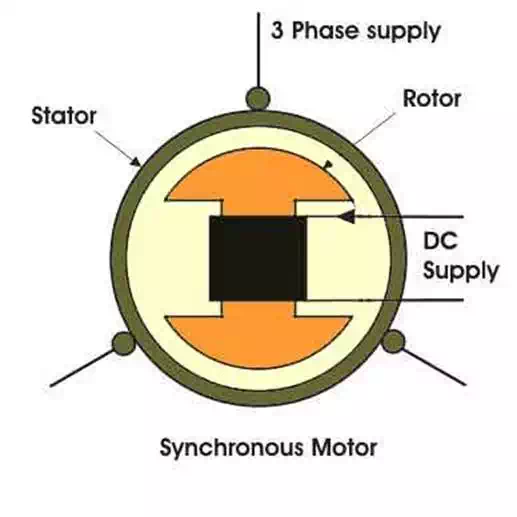
Now before knowing, how the synchronous motors are started, we should know why
they are not self
started? The answer can be given as, when 3 phase supply is given
to the stator, there is a rotating magnetic flux which rotates at synchronous speed, and if the rotor is
also given DC supply, rotor acts as a magnetic flux which rotates at
synchronous speed, and if the rotor is also given dc supply, rotor acts as a
magnet having two salient poles. As the rotor is at standstill position, it
cannot follow the magnetic field which is rotating at synchronous speed. The rotor stacks
at its position because the opposite poles move so rapidly that the rotor
locks, this is the reason why synchronous motors are not self starting.
Now coming to the point how synchronous motors are started. At first the
synchronous motors are started as a normal induction motors, the rotor of the
motor is not given dc supply, when the motor reaches the rotor and pull in
takes place, which is discussed later.
Another method
of starting the synchronous motor drives is by external motor. In this method
the rotor of the synchronous motor is rotated by an external motor and when the
speed of the rotor reaches near synchronous speed, the DC-field is switched on
and pull in takes place. In this method, the starting torque is very low and it
is not very popular method also.
Pull
in of Synchronous Motors
When the rotor
of the synchronous motors reaches near synchronous speed, then the DC field
supply is switched on and the pull in process begins. As during switching on
the DC supply due to the phase angle and torque angle there are various
disturbances seen in the motor and there are several slip of poles of air-gap
flux is also seen. As the pull in process is completed the rotor acquires
synchronous speed. The complete pull in as fast as possible the DC supply
should be switched on at the most favorable angle. Like
when the synchronous motor is running as induction motor, the DC supply should
be fed when the induction motor is at top speed, this will be the best moment
because the speed difference will be least at that point of time.
Braking of Synchronous Motors
As we know,
there are three types of braking i.e, regenerative, dynamic
and plugging type braking. But for synchronous motor drives only dynamic braking can be applied though
plugging can be applied theoretically. Regenerative braking cannot be applied
to them as they need higher speed than synchronous speed. Dynamic braking is
done by disconnecting the motor from supply and connecting it across a three
phase resistor. At that time the motor
works as a synchronous
generator and
energy is dissipated at the resistors. Plugging is not used for synchronous
motors as high plugging current can cause severe disturbance and damage in line.