Dynamics of Electrical Drives
When an electric motor rotates, it is
usually connected to a load which has a rotational or translational motion. The
speed of the motor may be different from that of the load. To analyze the
relation among the drives and loads, the concept of dynamics of electrical
drives is introduced.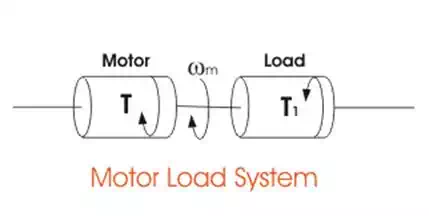
We can describe the dynamics of electrical drive easily by the following instant.
Here,
J = Polar moment of inertia of motor load
Wm = Instantaneous angular velocity
T = Instantaneous value of developed motor torque
T1 = Instantaneous value of load torque referred to motor shaft
Now, from the
fundamental torque equation -

For drives
with constant inertia,
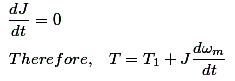
So, the above equation states that the motor torque is balanced by load torque
and a dynamic torque J(dωm/dt). This torque component
is termed as dynamic torque as it is only present during the transient
operations. From this equation, we can determine whether the drive is
accelerating or decelerating. Such as during accelerating motor supplies load
torque and additional torque component essentially. So, the torque, balancing
the Dynamics of electrical braking is very helpful.