Electrogas Welding (EGW)
Electrogas welding (EGW) is an vertical positioned
arc welding process, is used for welding the edges of sections vertically and
in one pass with the pieces placed edge to edge (butt joint). It is classified
as a machine-welding process, because for its operation requires special equipment.
The weld metal is deposited into a weld cavity between the two pieces to be
joined. The space is covered by two water-cooled copper dams(shoes) to prevent the
molten slag from running off; mechanical drives move the shoes upward.
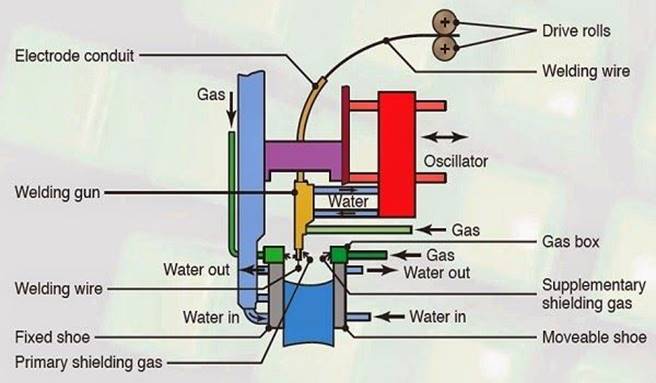
Schematic illustration of the electrogas welding
process.
One or
more electrodes are fed through a conduit and a continuous arc is maintained by
flux-cored electrodes at up to 750 A or solid electrodes at 400 A. Power
requirements is 20 kW. Shielding is done by means of an inert gas, such as
argon or helium depending on the type of material being welded. The gas may be
provided either from an external source, from a flux-cored electrode or from
both the sources. The equipment of electrogas welding is
reliable and training an operator is easy. Weld thickness is between 12 mm to
75 mm on steels, titanium and aluminum alloys.
Electrogas welding process is used in the
construction of bridges, pressure vessels, thick-walled and large-diameter
pipes, storage tanks, submarines and ships.