Bourdon tube Pressure Gauge
Principle of Bourdon tube pressure gauge:
when an
elastic transducer ( bourdon tube in this case ) is subjected to a pressure, it
defects. This deflection is proportional to the applied pressure when
calibrated.
Description of Bourdon tube Pressure Gauge:
The main parts of this instruments are as follows:
An elastic transducer, that is bourdon tube which
is fixed and open at one end to receive the pressure which is to be measured.
The other end of the bourdon tube is free and closed.
The cross-section of the bourdon tube is elliptical.
The bourdon tube is in a bent form to look like a circular arc. To the free end
of the bourdon tube is attached an adjustable link, which is in turn connected
to a sector and pinion as shown in diagram. To the shaft of the pinion is
connected a pointer which sweeps over a pressure calibrated scale.
Operation of Bourdon tube:
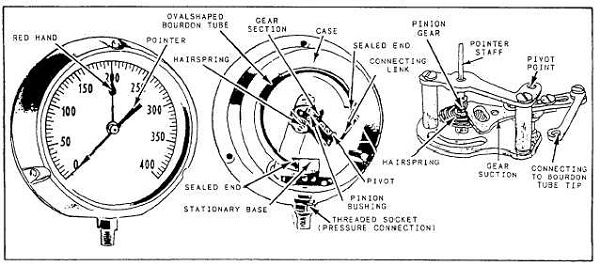
the pressure
to be measured is connected to the fixed open end of the bourdon tube.
The applied pressure
acts on the inner walls of the bourdon tube. Due to the applied pressure,
the bourdon tube tends to change in cross – section from elliptical to
circular. This tends to straighten the bourdon tube causing a displacement of
the free end of the bourdon tube.
This displacement of the free closed end of the bourdon tube
is proportional to the applied pressure. As the free end of the bourdon tube is
connected to a link – section – pinion arrangement, the displacement is
amplified and converted to a rotary motion of the pinion.
As the pinion rotates, it makes the pointer to assume a
new position on
a pressure calibrated scale to indicate the applied pressure
directly. As the pressure in the case containing the bourdon tube is usually
atmospheric, the pointer indicates gauge pressure.
Applications of Bourdon Tube pressure gauge:
They are used to measure medium to very high pressures.
Advantages of Bourdon tube pressure gauge:
These Bourdon tube pressure gauges give accurate results.
Bourdon tube cost low.
Bourdon tube are simple in construction.
They can be modified to give electrical outputs.
They are safe even for high pressure measurement.
Accuracy is high especially at high pressures.
Limitations of bourdon tube pressure gauge:
they respond
slowly to changes in
pressure
they are
subjected to hysteresis.
They are sensitive to shocks and vibrations.
Amplification is
a must as the displacement of the free end of the bourdon tube is low.
It cannot be used for precision measurement.