Steam (Thermal)
power Plant
A steam power plant,
also known as thermal power plant, is using steam as working fluid. Steam is
produced in a boiler using coal as fuel and is used to drive the prime mover,
namely, the steam turbine. In the steam turbine, heat energy is converted into
mechanical energy which is used for generating electric power. Generator is an
electro-magnetic device which makes the power available in the form of
electrical energy.
Layout of
steam power plant:
The layout of the
steam power plant is shown in figure below. It consists of four main circuits.
These are:
● Coal and ash circuit.
● Air and flue gas circuit
● Water and steam circuit and
● Cooling water circuit
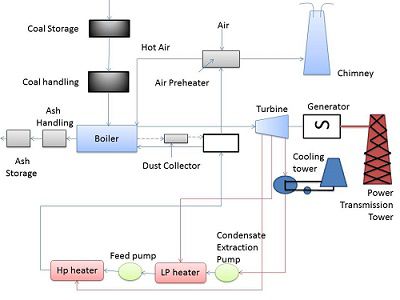
Coal and ash
circuit:
Coal from the
storage yard is transferred to the boiler furnace by means of coal handling
equipment like belt conveyor, bucket elevator, etc., ash resulting from the
combustion of coal in the boiler furnace collects at the back of the boiler and
is removed to the ash storage yard through the ash handling equipment.
Ash disposal :
The indian coal contains 30% to 40% ash. A power plant of
100MW 20 to 25 tonnes of hot ash per hour. Hence sufficient space near the
power plant is essential to dispose such large quantities of ash.
Air and flue
gas circuit:
Air is taken from
the atmosphere to the air preheater. Air is heated in the air preheater by the
heat of flue gas which is passing to the chimney. The hot air is supplied to
the furnace of the bolier.
The flue gases after
combustion in the furnace, pass around the boiler tubes. The flue gases then
passes through a dust collector, economizer and pre-heater before being
exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney. By this method the heat of the
flue gases which would have been wasted otherwise is used effectively. Thus the
overall efficiency of the plant is improved.
Air pollution:
The pollution of the
surrounding atmosphere is caused by the emission of objectable gases
and dust through the chimney. The air pollution and smoke cause nuisance to
people surrounding the planet.
Feed water and
steam circuit:
The steam generated
in the boiler passes through super heater and is supplied to the steam turbine.
Work is done by the expansion of steam in the turbine and the pressure of steam
is reduced. The expanded steam then passes to the condenser, where it is
condensed.
The condensate
leaving the condenser is first heated in a l.p. water heater by using the steam taken from the
low pressure extraction point of the turbine. Again steam taken from the high
pressure extraction point of the turbine is used for heating the feed water in
the H.P water heater. The hot feed water is passing through the economizer,
where it is further heated by means of flue gases. The feed water which is
sufficiently heated by the feed water heaters and economizer is then fed into
the boiler.
Cooling water
circuit:
Abundant quantity of
water is required for condensing the steam in the condenser. Water circulating
through the condenser may be taken from various sources such as river or lake,
provided adequate water supply is available from the river or lake throughout
the year.
If adequate quantity
of water is not available at the plant site, the hot water from the condenser is
cooled in the cooling tower or cooling ponds and circulated again.
Advantages of
thermal power plants
1. Initial cost is low compared
with hydro-plant.
2. The power plant can be located
near load center, so the transmission losses are
considerably reduced.
3. The generation of power is not
dependent on the nature’s mercy like hydro plant.
4. The construction and
commissioning of thermal plant requires less period of time than a hydro plant.