V Belts
Lets us begin with a basic question.
How do we transmit rotary power from one place to another? Well we have numerous
solutions and one of the solutions would surely be a V-Belt. A simple way of
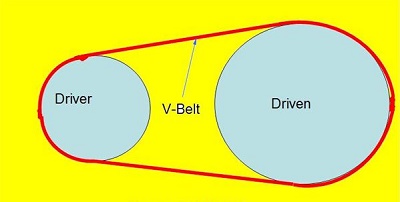
defining any belt drive would be imagining two separate rollers being bound by
means of a thread that runs over its outer periphery. The thread acts as the
power transmitter conveying power from the driver member to the driven member.
In the actual V-Belt drive system, the thread is the V-Belt and the rollers are
called as pulleys.
V-Belts are friction based power or
torque transmitters. The power is transmitted from one pulley to the other by
means of the friction between the belt and pulley. The rubber used as the base
material plays a very vital role in this. This is quite similar to the friction
between the Tyre and road in the automobiles that enables the automobiles to
move on the road.
The V-Belt is
called so because of its cross section. The cross section of a V-Belt is
similar to that of the letter V. Let us know look into the constructional aspects
of the V-Belt. The V- Belt consists of the following
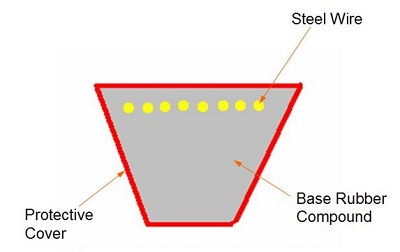
1. Steel Wires: The wires are of endless type having no joints in them. They provide the necessary reinforcement and strength to the V-Belt for transmission of the torque.
2. Base Rubber Compound: The wires are surrounded by a special rubber compound providing shape to the V-Belt. The compound also acts as a compression medium to absorb the shocks during power transmission.
3. Protective Cover: The protective cover is basically a layer of plastic which provides endurance for the rubber against the high temperature that is generated during the movement of the v-belt.
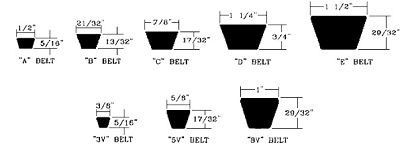
The V-Belts are basically classified
into 5 types or sections i.e. A, B, C, D and E. The categorization of
this is based on the cross sectional size of the belt and the amount of power
to be transmitted by the belt. The dimensions of various sections of the V-belt
are shown below. The included angle of the V-Belts is 40 Degrees.
Heres is a brief outline on the
power transmitting capacity of the each section type of the belt. The exact
transmission power of the belt will vary based on other criteria like arc of
contact, speed ratio, etc.
Section A Type - 0.1 kW to 3 kW
Section B Type 0.5 kW to 6 kW
Section C Type 1 kW to 12 kW.
Section D Type - 3 kW to 32 kW.
Section E Type 5 kW to 50 kW.
The values above indicate the
capacity of a single belt. In case a higher power is to be transmitted. The
belt can always be coupled with more belts in series to transmit the required
torque.
How is a V Belt Specified?
Heres a typical example of its
specification C 2032" . Here the C denotes the section type of the
belt, 2032 represents the nominal inside length of the belt,
Here are some of the features or
advantages of V- Belts
1. They transmit higher torque with lesser width and tension
compared to other type of belts.
2. They can be used in areas with very less arc of contact of
the belt.
3. They can be operated in speeds ranging between 5 to 30
m/sec.
The disadvantage of the V belt is
that, due to the wedging action of the belt and increased bending and windage
losses the efficiency of the belt is about 3% lesser than the other type of
belts. Apart from this the belt does have the tendency to slip at high loads
and gets easily damaged during slipping.