Types of Flexible Coupling – Gear
Couplings
Couplings are used as connecting
elements between two shafts. The complexity in the type of connectivity, the
power to be transmitted and the area of application tend to play a vital role
in the selection of the type of the coupling.
Gear Couplings
belong to the category of flexible couplings that are capable of transmitting
very high torques. Constructionally the gear coupling utilizes the advantages
of gear engineering; practically the coupling is a complete gear assembly. Let
us now look into the constructional aspects of the coupling.
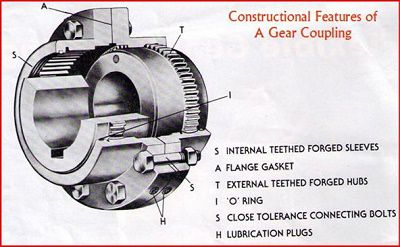
1. The gear couplings consists of a forged sleeve with
internal teeth cut on its inside. The forged sleeves are normally two halves
possessing internal gears in both of them. In certain cases the forged sleeve
tends to remain a single piece.
2. Two hubs with external teeth containing the same number of
teeth as in the internal gear is present with each one being mounted on the
driven and driver shaft respectively. The tooth profile of the external teeth
is normally crowned in order to take up more loads.
3. The entire assembly in normally enclosed and is provided
with gaskets at the joints and O-rings at vantage points in order to prevent
the leakage of the lubricant filled inside the coupling,
4. Lubrication plugs are provided at vantage points in order
to lubricate the couplings during predetermined intervals of time.
Tooth forms in the Coupling:
Three types of external teeth are
used in gear couplings. The only difference is the manufacturing methodology of
the same.
a.) Straight Teeth: The external teeth in the hub are straight. During the condition of misalignment in the coupling the contact pattern between the internal gear and the external gear tends to be line type of contact.
b.) Crowning with constant radius:
The external teeth are barrel shaped with a constant radius in order to
increase the area of contact and move the area of contact to a near middle
portion of the teeth.
c.) Crowning with variable radius:
The external teeth are barrel shaped with a variable radius instead of constant
radius. This increases the area of the contact significantly compared to that
of the constant radius crowning.
The maximum degree of misalignment permissible
in gear couplings is from 0.5 Degrees to 1.5 Degrees. This varies with the size
of the coupling being used.
Selection procedure for gear
coupling:
The gear couplings are selected based
on the torque ratings.
● 1. The torque transmitted by the coupling is to
be determined.
● 2. Based on the application the appropriate service factor needs to be determined.
3. The equivalent torque is to be determined by
multiplying the service factor with the torque transmitted.
4. Select the coupling
based on the equivalent torque value calculated. A reference selection chart is
given below for example.
