Eliminating Vibration Problems in Piping
Whether
installed on a ship, factory, or in the local supermarket, all piping needs to
well supported and vibration free. Pipe supports can incorporate springs to
reduce vibration, however there are numerous other designs of specific
vibration eliminators that can be fitted to the pipework.
Piping
runs require careful alignment through the proper use and location of
anti-vibration elements, expansion joints along with pipe supports, pipe shoes,
and guides. These basic requirements will make sure that the installed pipework
will carry the liquids safely and without leaks.
Overview of Pipe Installation Techniques
Always
investigated any vibrating pipework with some urgency. The problem was normally
pipe support clamps working loose, spring hangers or machinery anti-vibration
mountings (AVM’s) needing readjustment, or machinery coupling misalignment.
The
urgency to find the cause was due to the damage that could be done to the
piping runs: cracked pipes, leaking flanges, or malfunction of associated
equipment.
Piping
installation is a specialist trade and should be left to the piping engineer
and his team of pipe-fitters, however most mechanical/production engineers are
familiar with the basics that follow.
Pipes are
fabricated to isometric drawings and full material traceability of
the pipe and pipe fittings is required by piping standards. Once fabricated the
pipes are painted prior to being fitted as per the installation drawings. If
the fluids being carried in the pipe are subjected to temperature fluctuation,
expansion bends will be incorporated along with expansion bellows or
expansion gimbals that allow the safe expansion and contraction of the
pipework.
Pipe
guides and shoes are fitted to the pipe to ensure the piping remains axially
aligned, with the spider type being the most popular and reliable type.
Piping Vibration Analysis – An Overview
Before we
examine the various types of anti-vibration components available to engineers,
it is important that we have a quick look at vibration analysis and management.
The
analysis comprises of running up the pumps supplying the piping to achieve the
optimum pressure and temperature setting. A vibration monitor/transducer that
records the frequency and acceleration of motions is attached securely to the
pipe and a measurement taken and recorded. This is repeated at different
locations every 12’ or so along the pipe run determining the pipe motions in
the X, Y, and Z axis.
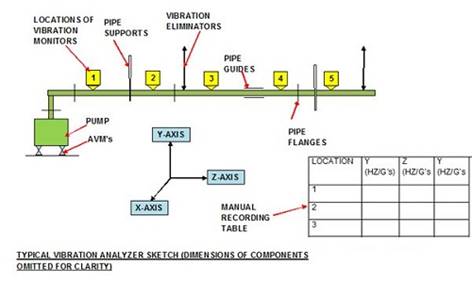
A sketch
showing the location of the transducer along with the location of flanges, pipe
supports and any expansion/anti-vibration components is then drawn. This may be
done manually (in my day) or automatically, depending on accessories
incorporated within the more modern transducer.
A typical
sketch for to produce the vibration analysis manual modular plot is shown
below, along with a section of a manual recording sheet. (Please click on image
to enlarge.)
Types of Modern Anti-vibration Components Used in Piping
Installations.
There are
two basic categories of anti-vibration components, these being in-line and
hanging.
1. In-line Devices
·
Bellows
These consist of a
set of accordion-like steel bellows that are designed and rated for different
weights of piping. The bellows are encompassed between two flanges used to bolt
the component into the piping run. An example of this is shown below:
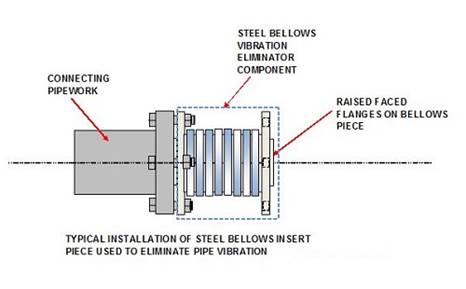
·
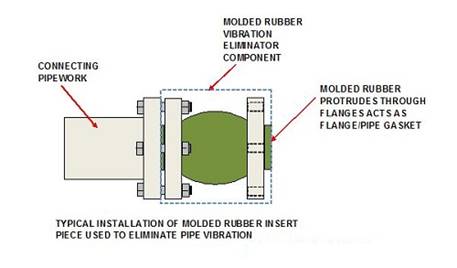
Rubber Molded Section
This
comprises an oval molded section
between two flanges that are used to bolt the component into the pipework.
The molded rubber
protrudes through the flanges and is used as a gasket. A typical application is
shown below:
2. Hanging Devices
·
Sprung Hanger
The
device is designed to incorporate a pipe support and clamp. The springs are
rated for various types of pipe anti-vibration control, being adjustable
through a set of locknuts on the threaded bar hangers. A typical example is
shown below:
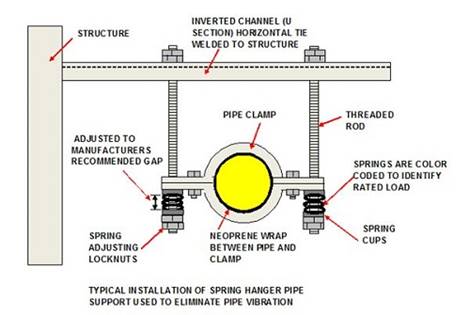
·
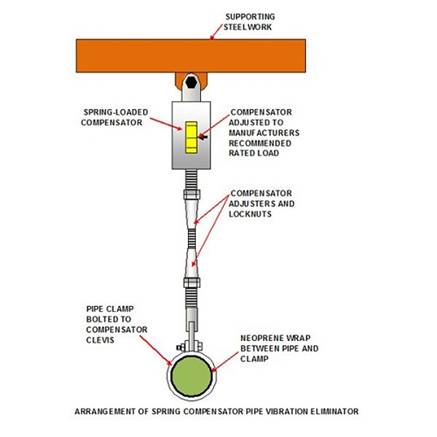
Spring Compensating
This
design also incorporates a pipe support, but only one spring is used between
the structure and the piping. The compensating spring is held within a casing
and is adjustable using bottle screws or some such method. These are available
in numerous ratings to suit most piping applications, and a typical application
is shown below:
Summary
Piping
runs are all subject to an amount of vibration, it is excessive vibration that
will cause the failure of the pipe and the components connected to it.
Anti-vibration
measures can be put in place to prevent this and these can be put into two
categories; in-line and hanging. \the in line are usually comprised of
resilient materials in a section enclosed by two flanges. The hanging types are
mainly sprung and incorporate pipe supports and clamps. As well as
anti-vibration components, pipe guides, supports along with expansion joints
and bends are required to obtain the optimum efficiency from the piping run.