Five Useful Tips for Plastic Part Design
Plastic
part design is a specialized job and a little different than product design
using metals. Five important tips for plastic part product design and
engineering will be discussed in this article.
From your
car to your computer, you will find the use of plastic parts in almost
everything everywhere around you. Most of the plastic parts are manufactured by
some type of molding process. As a design
engineer, the following five tips will be handy for designing plastic parts:
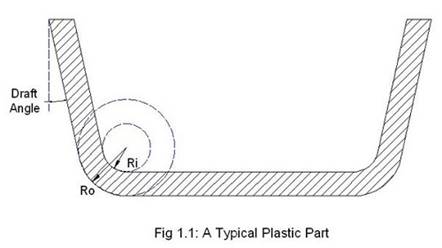
1. Draft Angle: Draft angle is the
slant angle of a plastic part (as shown in the picture above). Providing a
proper draft angle is important for the (easy) removal of the plastic part from
a mold.
Draft angle should be as much as possible.
Standard
practice is having a draft angle of 1 to 2 degrees if there are no textures or
lettering in the surface. In case of lettering and textures, an additional
draft angle of 1.5 degrees per 0.025 mm depth of the texture is recommended.
2. Wall thickness: While
designing the plastic parts, design it for the wall as thin as possible. The
thicker the wall, the slower the cooling rate and the greater the chance of
getting defective plastic parts. If you need a thicker wall, go for it but make
sure the wall thickness is uniform throughout the part. In case you cannot
avoid uneven wall thickness, then assure gradual changes in the thickness.
3. Radius: Avoid sharp corners
in order to minimize stress concentrations and molding defects in the
designed plastic part.
The
recommended value of radius is at least equal the thickness of the plastic
part. And the centre point for the internal and the external radius should
coincide. In other words, external radius = internal radius + thickness.
4. Rib: One method of
avoiding warpage in plastic part is providing one or more ribs in the design.
At the same time, the thickness of ribs should be kept to minimum or it will be
subjected to molding defects
like shrinkage.
The
thickness of the rib should be in between ½ to 1½ times the wall thickness of
the plastic part. The height of the rib should be less than three times the
thickness of the plastic part. A one degree taper angle is recommended for rib
design.
5. Boss: Sometimes you may
have to design plastic parts with bosses. Standard practices for designing
bosses in your plastic part are:
6. The ratio of the
outer diameter to the inner diameter of the boss should be between 2 to 3.
7. The boss wall
thickness should be around ½ to 1½ the wall thickness of the plastic part.
8. The height of the
supporting gussets for the boss should be around 2/3 the height of the boss
itself.
9. The taper angle for
the boss should be around 1 degree.
Conclusion
The
plastic part design procedure has some similarities with casting design.
However, the thickness of casting components is normally higher than that of
plastic parts. CAD modeling of
the plastic part can be done using ProE or Unigraphics. However
specialized CAD packages are also available.