Break-even Analysis
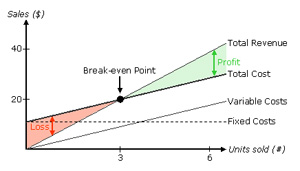
The break-even analysis in production management and industrial engineering consists of total cost (i.e. fixed cost and variable cost) and sales revenue.
A break-even analysis is a financial tool which
helps you to determine at what stage your company, or a new service or a
product, will be profitable. In other words, itís a financial calculation for
determining the number of products or services a company should sell to cover
its costs (particularly fixed costs). Break-even is a situation where you are
neither making money nor losing money, but all your costs have been covered.
Break-even analysis is useful in studying the relation
between the variable cost, fixed cost and revenue. Generally, a company with
low fixed costs will have a low break-even point of sale. For an example, a
company has a fixed cost of Rs.0 (zero) will automatically have broken even
upon the first sale of its product.
Components of Break Even Analysis
Fixedcosts
Fixed costs are also called as the overhead cost. These
overhead costs occur after the decision to start an economic activity is taken
and these costs are directly related to the level of production, but not the
quantity of production. Fixed costs include (but are not limited to) interest,
taxes, salaries, rent, depreciation costs, labour costs, energy costs etc.
These costs are fixed no matter how much you sell.
Variablecosts
Variable costs are costs that will increase or decrease in
direct relation to the production volume. These cost include cost of raw
material, packaging cost, fuel and other costs that are directly related to the
production.