Radio Frequency Ensures Various Identifications
RFID identifies tracking, recording, storing of products, and communicating fast important business issues.
Radio frequency identification
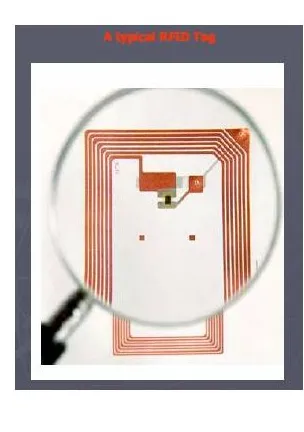
Radio frequency identification is known as RFID TAG. The tag is incorporated into persons, products, and animals, and serves in identifying using radio waves. Tags can be read from several meters away using radio waves. Radio-frequency identification uses interrogators, which are known as readers. "Label" is another word sometimes used for an RFID tag.
Radio frequency identification is a powerful technology that can help companies achieve total business visibility. RFID can identify the location of assets, tools, inventory, and people. Companies can optimize business processes which reduces operational costs.
The method of identification is to store a serial number which identifies a person or object. The RFID transponder- the tag or label- has a chip and the antenna together. The antenna transmits information to the reader. Radio waves are reflected back from the tag and are passed on to computers.
The price of tags is based on volume, memory power, and packaging or whether encased or embedded in a label. The price varies from 7 to 15 US cents. If the tags are embedded in thermal transfer labels, the costs may be 15 cents or more. High frequency tags cost a little more.
The waves beamed back to the computer resemble a fingerprint, which identifies the object with the tag. RF energy is used for communications of data by using without RFID tag. However the silicon microchip in the tag does not store a serial number. Conductive polymers, or plastic are used without chip tags.
The common purpose of RFID identifies tracking, recording, storing of products and communicating fast important business issues. AIM is automatic identification and mobility technology. AIM is the main function of the radio frequency identification system. It provides quick and correct information data entry.
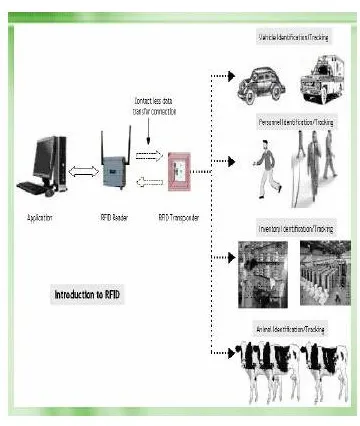
Multiple uses of RFID
RFID system is used for tracking cars and vehicles, identifying people, controlling machines, and tracking cattle.
For example, consider a small, general purpose RFID tag embedded in a user's finger or arm. In an auto-managed library, smart human profile matching while relaxing in a chair is remote controlled by RFID. People come and go in the library hall. Their coming and going is tracked by RFID tags. The inventory of books is also precisely maintained.
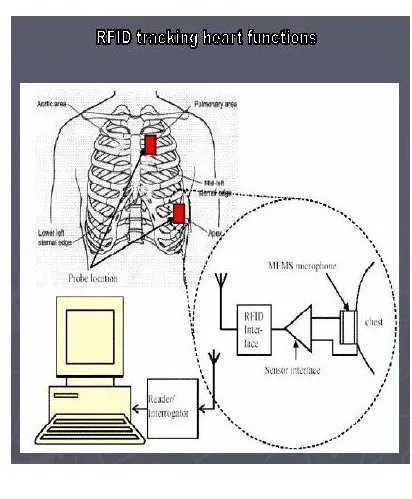
The hot axle of a train is monitored by remote controlled RFID tags. When the wheel bearing becomes hot and seizes, an alarm prompts the engine driver to immediately stop the train and RFID averts a major accident. The RFID control tags are installed along the tracks. The tags have auto heat sensors. They give an alarm when the wheel roller bearings get hot.
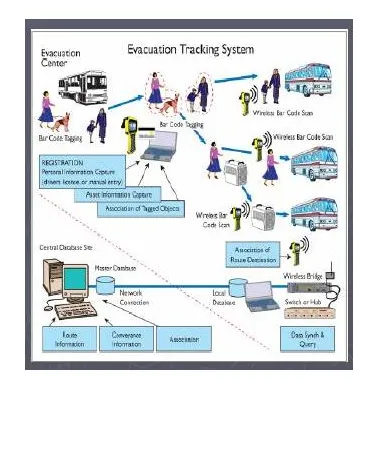
Manufacturing a polyurethane vehicle seat is remote controlled while pouring polyurethane into the seat bags. RFID efficiently manages evacuation of people from floods affected areas shifting the people to safer locations. Bus services are RFID controlled managing timely services, and their booking for various destinations. RFID assets of cargos at the shipping yard are automatically managed by remote controls. At a busy bar, people are tracked, and there is no scope for them hiding within the bar premises.
Mobility of AIM system is subject to customers choices. Performance has to be guaranteed. Appropriate National and International Standards are formulated for RFID Technology. Practical training is rendered to RFID guides. Research continues to achieve perfection level at lower costs. Application and Technological Standards are further fortified. The trend of utility has increased beyond expectations.