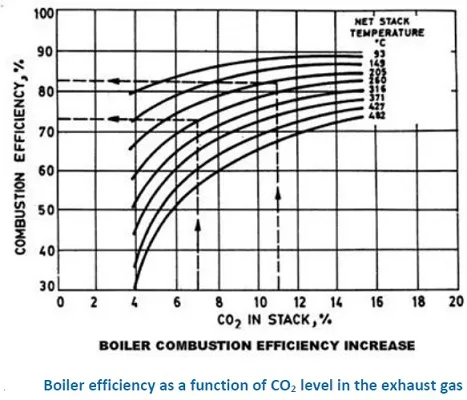
Fig (ii): Boiler efficiency as a function of CO2 level in the exhaust gas
Excessive combustion air
Fig (ii): Boiler efficiency as a function of CO2 level in the exhaust gas
In order to burn the fuel, air needs to be supplied to the boiler. The excess air unused in the combustion gets heated and then discharged through the chimney. This is waste of energy. Thus, any excess air that is not needed for combustion will cause energy loss as it will take away heat from boiler and discharge to the atmosphere, thus normally should be avoided.
Boilers normally have certain amount of optimal excess air and the air input must be adjusted to this level. It signifies a balance between combustion efficiency and amount of air supplied. Excessive “excess air” is identified in the form of either high O2 concentration or low concentration of CO2 in the boiler exhaust gas. These two parameters thus need to be monitored as part of controlling boiler excess air thus its energy efficiency. Figure (ii) shows the boiler efficiency as a function of CO2 concentration. As can be seen, it is desirable to maximise the CO2 concentration in the exhaust gas for best efficiency. As indicated, the optimum level would normally be specified by the manufacturer.