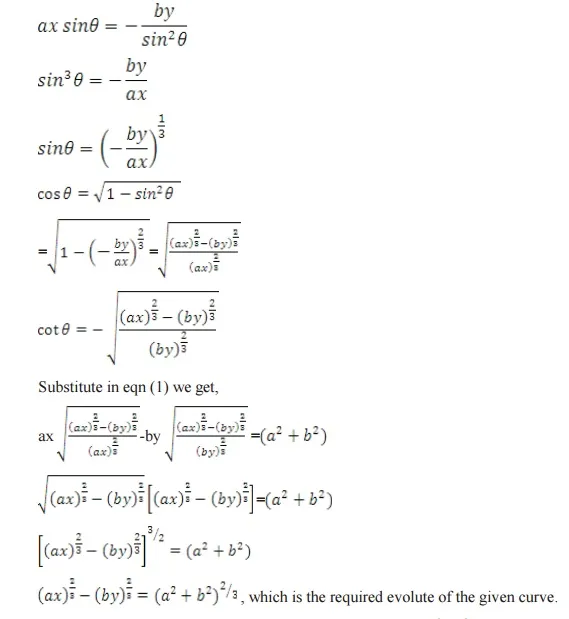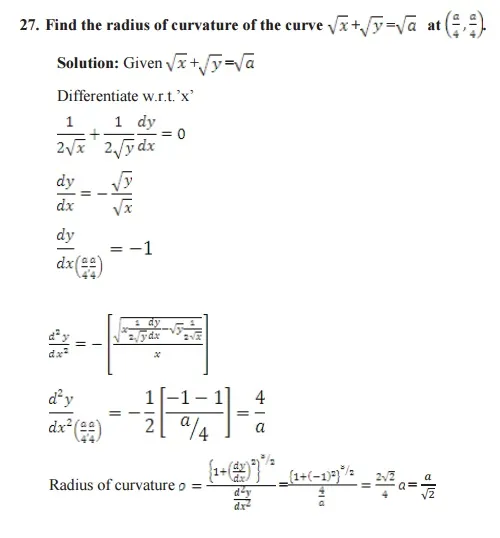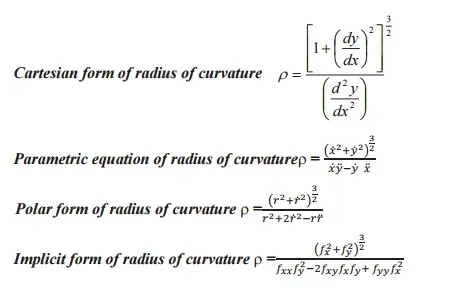
DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
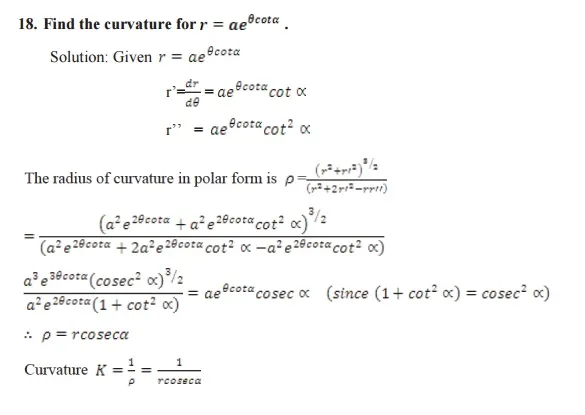
Curvature: The rate of bending of a curve in any interval is called the curvature of the curve in that interval.
Curvature of a circle: The curvature of a circle at any point on it equals the reciprocal of its radius.
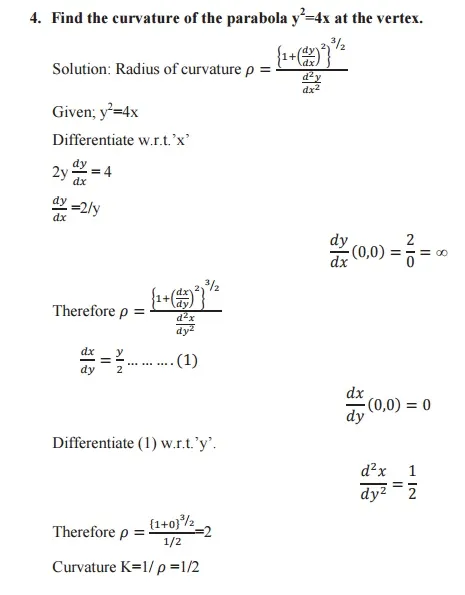
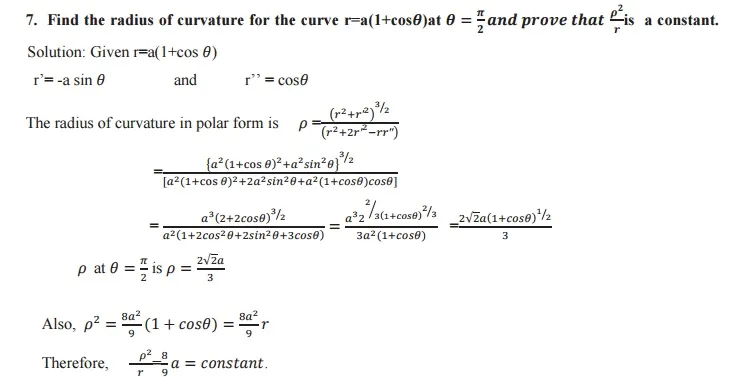
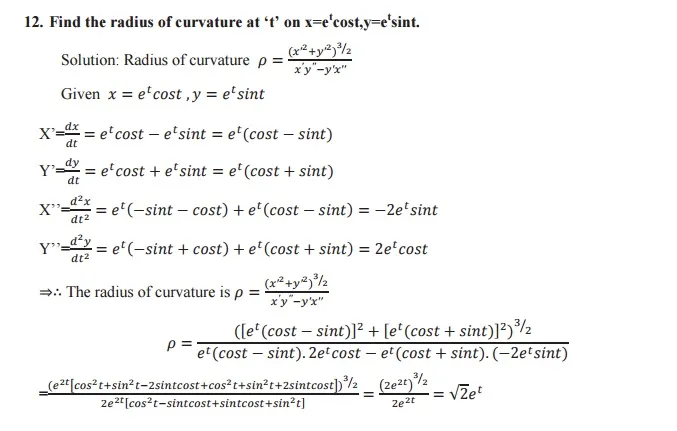
Radius of curvature: The radius of curvature of a curve at any point on it is defined as the reciprocal of the curvature

Centre of curvature: The circle which touches the curve at P and whose radius is equal to the radius of curvature and its centre is known as centre of curvature.
Equation of circle of curvature:
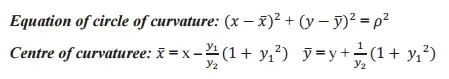
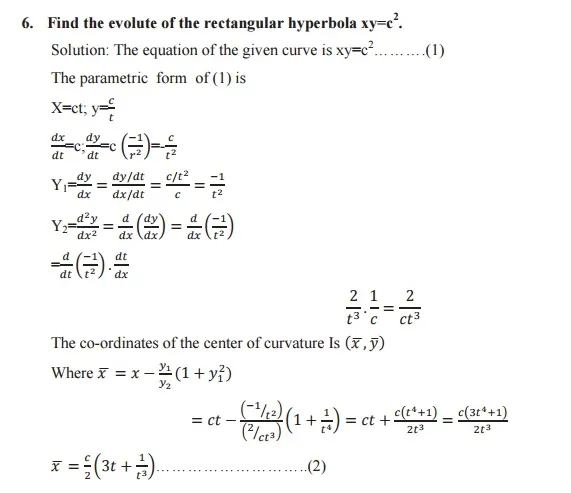
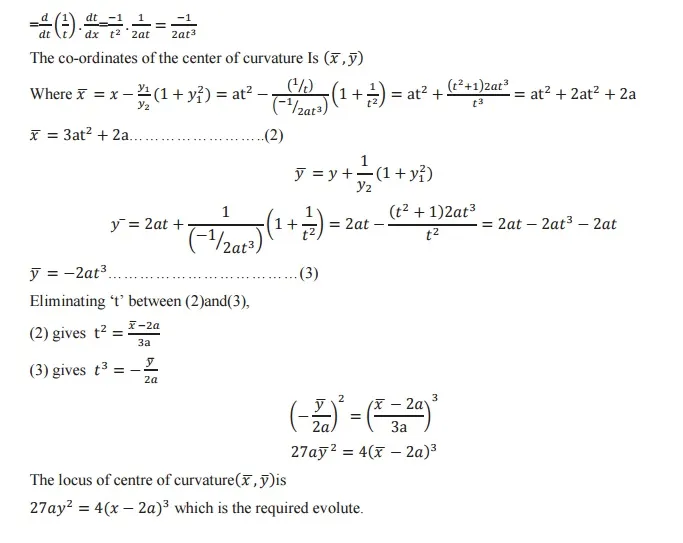
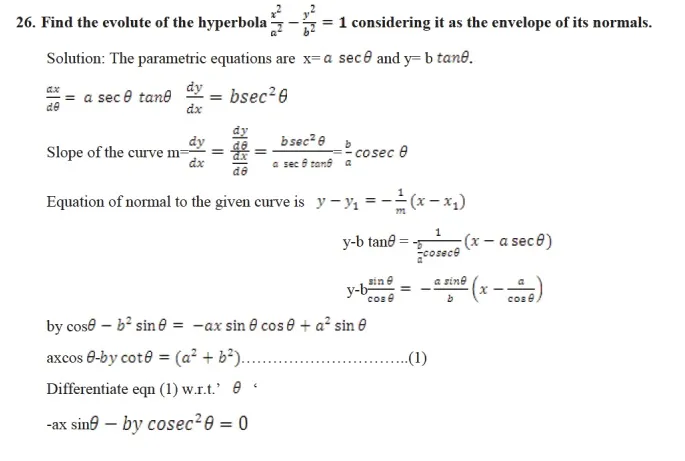
Evolute: The locus of the centre of curvature is called an evolute
Involute: If a curve C1 is the evolute of C2 , then C2 is said to be an involute of a curve C1.
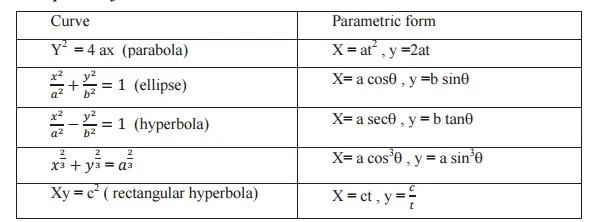
Parametric equation of some standard curves
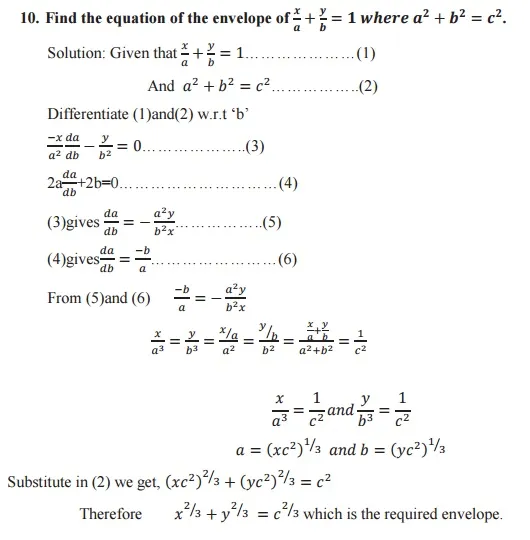
Envelope: A curve which touches each member of a family of curves is called envelope of that family curves.
Envelope of a family of curves: The locus of the ultimate points of intersection of consecutive members of a family of curve is called the envelope of the family of curves.
Properties of envelope and evolute
Property:1: The normal at any point of a curve is a tangent to its evolute touching at the corresponding centre of curvature.
Property:2 The difference between the radii of curvature at two points of a curve is equal to the length of the arc of the evolute between the two corresponding points.
Property:3: There is one evolute ,but an infinite number of involutes
Property:4 The envelope of a family of curves touches at each of its point. The corresponding member of that family
Evolute as the envelope of normals: The normals to a curve form a family of straight lines.we know that the envelope of the family of these normals is the locus of the ultimate points of intersection of consecutive normals. But the centre of curvature of a curve is also the point of consecutive normals. Hence the envelope of the normals and the locus of the centres of curvature are the same that is ,the evolute of a curve is the envelope of the normals of the curve.