Engine Room Crane
Describe the safeties associated with Engine Room Crane?
§ Push button type controller remote.
§ Emergency stop is provided.
§ Limit switches are provided, 2 for each transverse, longitudinal and up-down movement.
§ Mechanical stoppers are provided, if in case limit switch will fail.
§ Load limit switch is provided, to prevent the overloading of crane(by weight).
§ Electromagnetic fail safe brake system is provided, which will prevent any movement of hook when it is not in operation or in case of power failure.
§ Overloading and thermal protection of motor is provided for motors in it.
§ Crane hook is provided with self locking arrangement.
§ Safe Working Load(SWL) is marked on it, which is much lower than the load test weight. And weight above this should not be carried by it(SWL certificate).
§ All other equipment like sling, d-shackle etc. are provided with SWL certificate.
Explain how does Emergency Fail Safe Brake System works?

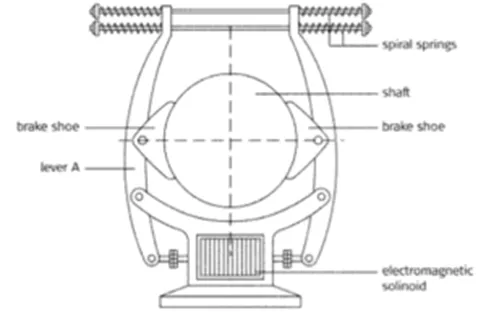
Emergency Fail safe Brake System is also called as centrifugal/ Electromagnetic brake system. Electromagnetic brakes are usually found on machines like cranes and lifts, and they work as back-up braking systems. These brakes only work when the electricity supply stops, to make sure that, for example, the load carried by the crane, that moves up and down in a building, doesn’t fall if the load that the crane was carrying fell. The main parts are :
§ 2 Brake shoes
§ 2 Levers
§ 2 Spiral springs
§ Electromagnetic solenoid
The braking action of an electromagnetic brake works as follows:
§ When the electricity is flowing, the electromagnetic solenoid uses magnetic force to pull the two levers in towards it, which keeps the springs attached to the top of the levers open.
§ The open springs keep the brake shoes, which are positioned on each side of a shaft, away from the shaft while it is turning.
§ When the electricity stops flowing, the electromagnetic solenoid stops working. With the magnetic force gone, the spiral springs close, which pushes the brake shoes against the shaft to stop it from turning.
Describe how limit switch are operated in crane operation ?
A limit switch is a critical component of overhead crane safety. There are different kind of limit switch. A limit switch keeps a crane from lifting loads above rated capacity. Another kind of limit switch prevents a hoist from reaching the upper block and rope drum. There are multiple limit switches associated with a crane operation such as crane travel or hoist motion. The switch will signal that the end of the safe travel limit has been reached, and stops the motion.
After being tripped by the ultimate limit (cargo crane, normally not in engine room crane same for emergency stop) may require a manual reset. This involves resetting a wedge component or lever so that an inspection can be carried out to determine why the crane reached this position and did not stop at the up stop limit position.
Describe routine checks on engine crane?
Before carrying out any operation using engine room crane
§ Check the lubrication
§ Check the brake operation
§ Check condition of clamp in the hook
The routine maintenance of crane according to running hours by the makers:
§ Check the noise level by operating it without load
§ Check the heat generation
§ Check all the limits and trips
§ Check the contact areas of electrical equipment
§ Overhauling of motor
§ Greasing of wires
§ Renewal of wire ropes
§ Annual survey
§ Load test
Describe routine checks and works carried out on engine crane by parts?
Gears:
§ Gear case oil condition (replenish it with fresh lube oil if needed)
§ Gear case noise
§ Gear teeth inspection
Sheave:
§ Inspect the groove which is in contact with the wire for wear down
§ The sheaves for freedom of rotation
§ The trueness of sheaves. It may bend if the load is lifted obliquely
§ Check for cracks and broken circumference on the face of the sheave
§ Check the bearings provided in the sheave assembly
§ Check the bolt and the pin holding the sheave in place are in good condition
§ Check each sheave to insure rope groove is smooth and free from burrs, or other surface defects
Hook :
§ Lubrication of bearing
§ Make sure the dowel pin holding the hook is in position. Measure the pin diameter and replace if its worn out
§ Ensure safety latch spring is in working condition to avoid jumping of load
§ If rotation lock is provided, check its operation
§ Check the material for brittleness, cracking and hardness during survey
§ If the part used for rigging the rope has worn out, check its shape (concave) and repair or replace as per the condition
Brake:
§ Measure the distance between magnet and armature.
§ Adjust the braking power nut to reach the required gap (if faulty).
§ Check for the moisture on the surface of the lining of electromagnetic brake to avoid slippage
§ Check for signs of overheating and mechanical damages
§ Check the tension of spring which carries the brake during overhauling of the brake assembly
Wire Ropes:
§ Wind the wire rope in correct way to prevent kink of the rope
§ Lubricate the wire rope at regular interval