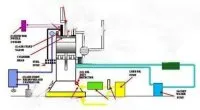
ENGINE ROOM SYSTEMS AND LAYOUT

Engine room is the heart and muscles of a ship, providing necessary power and essential “fluids” for a modern vessel. Usually a merchant ship has propulsion and auxiliary power generators in engine room or dedicated compartments as for steering or separators. There are different systems and installations to keep vessel safe and running. They may differ from ship to ship so will mention few that can be found in most:
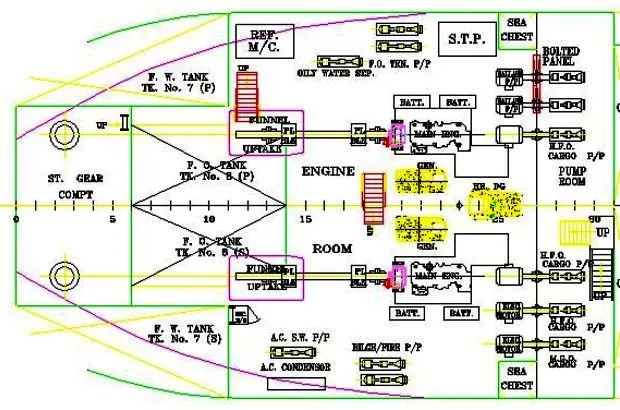
1. propulsion system
a. main engine(s) or turbine(s)
b. gear(s)
c. shaft line(s)
c. propeller(s)
d. CPP system
2. power generation system
a. auxiliary engines or turbines
b. shaft generator(s)
c. emergency generator
d. port generator
3. fuel systems
4. lubrication oil systems
5. cooling systems
6. heating systems (boilers, other heating systems)
7. gas exhaust systems
8. starting systems
9. bilge and ballast systems
10. ventilation systems
11. cargo systems (for liquid cargo)
12. domestic systems
a. fresh water system
b. seawater water system
c. waste system (black water, grey water, incinerator)
Not to forget all piping and electrical systems to be run in the engine room following all safety rules.
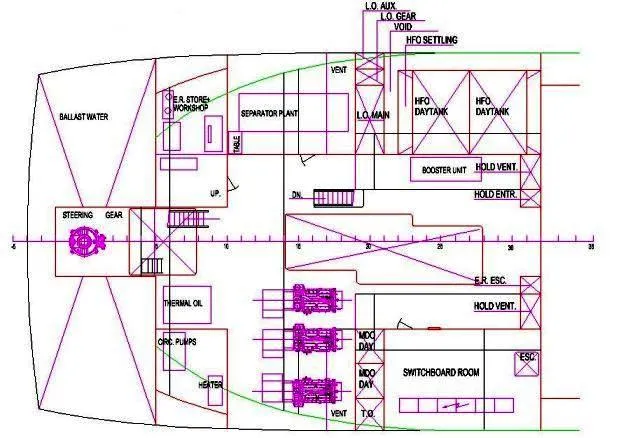
As you can see in the examples the arrangement of an engine room is similar to most ships when thinking to basic systems. Different parts of the systems are arranged and fixed using engine room horizontal and vertical space, on decks or platforms. All components and machineries have to be arranged in such a way to use at maximum their characteristics, to allow circulation spaces, servicing and dismantling/replacing spaces.
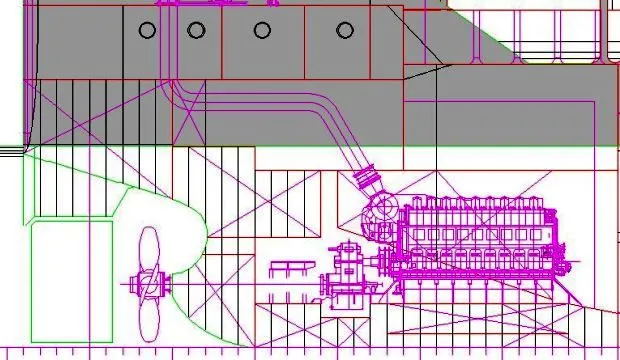
About specific systems, parts and components in next articles.