CHEMICAL MACHINING
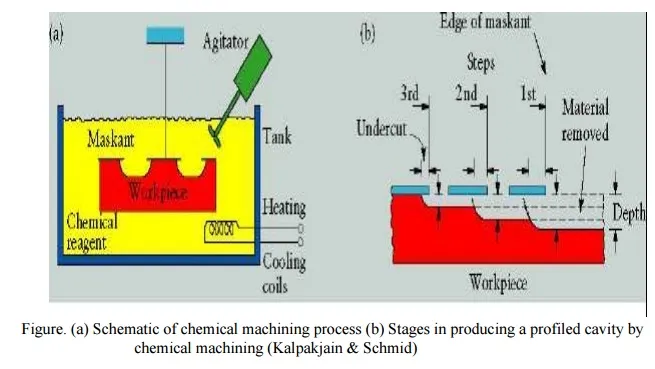
Chemical machining (CM) is the controlled dissolution of work piece material (etching) by means of a strong chemical reagent (etchant). In CM material is removed from selected areas of work piece by immersing it in a chemical reagents or etchants; such as acids and alkaline solutions. Material is removed by microscopic electrochemical cell action, as occurs in corrosion or chemical dissolution of a metal. This controlled chemical dissolution will simultaneously etch all exposed surfaces even though the penetration rates of the material removal may be only 0.0025–0.1 mm/min. The basic process takes many forms: chemical milling of pockets, contours, overall metal removal, chemical blanking for etching through thin sheets; photochemical machining (pcm) for etching by using of photosensitive resists in microelectronics; chemical or electrochemical polishing where weak chemical reagents are used (sometimes with remote electric assist) for polishing or deburring and chemical jet machining where a single chemically active jet is used. A schematic of chemical machining process is shown in Figure.

Figure. (a) Schematic of chemical machining process (b) Stages in producing a profiled cavity by chemical machining (Kalpakjain & Schmid)