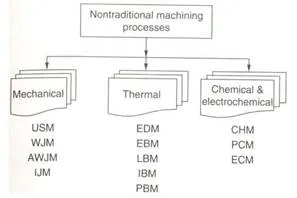
Classification of Non-Traditional Machining
These can be classified according to the source of energy used to generate such a machining action: mechanical, thermal, chemical and electrochemical. Mechanical: Erosion of the work material by a high velocity stream of abrasives or fluids (or both) Thermal: The thermal energy is applied to a very small portion of the work surface, causing that portion to be removed by fusion and/or vaporization of the material. The thermal energy is generated by conversion of electrical energy. Electrochemical: Mechanism is reverse of electroplating. Chemical: Most materials (metals particularly) are susceptible to chemical attack by certain acids or other etchants. In chemical machining, chemicals selectively remove material from portions of the workpart, while other portions of the surface are protected by a mask.
Classification of Non-Traditional Machining

Mechanical Machining
• Ultrasonic Machining (USM) and Waterjet Machining (WJM) are typical examples of single action, mechanical non traditional machining processes.
• The machining medium is solid grains suspended in an abrasive slurry in the former, while a fluid is employed in the WJM process.
• The introduction of abrasives to the fluid jet enhances the machining efficiency and is known as abrasive water jet machining. Similar case happens when ice particles are introduced as in Ice Jet Machining.
