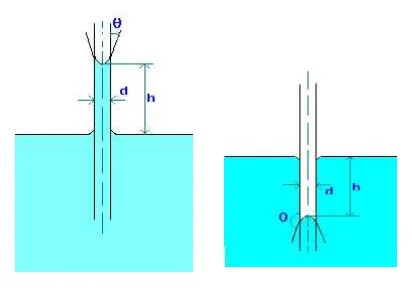
CAPILLARITY
Capillarity is defined as a phenomenon of rise or fall of a liquid surface in a small tube relative to the adjacent general level of liquid when the tube is held vertically in the liquid. The rise of liquid surface is known as capillary rise while the fall of the liquid surface is known as capillary depression.
It is expressed in terms of cm or mm of liquid. Its value depends upon the specific weight of the liquid, diameter of the tube and surface tension of the liquid.

1.Water has a surface tension of 0.4 N/m. In a 3 mm diameter vertical tube if the liquid rises 6 mm above the liquid outside the tube, calculate the contact angle.
Data:
Surface tension (s) = 0.4 N/m
Dia of tube (d) = 3 mm = 0.003 m
Capillary rise (h) = 6 mm = 0.006 m
Formula:
Capillary rise due to surface tension is given by
h = 4 cos(q)/(rgd), where q is the contact angle.
Calculations:
cos(q) = hrgd/(4s) = 0.006 x 1000 x 9.812 x 0.003 / (4 x 0.4) = 0.11
Therfore, contact angle q = 83.7o