DARCY’S EQUATION FOR LOSS OF HEAD DUE TO FRICTION IN PIPE
A pipe is a closed conduit through which the fluid flows under pressure.When the fluid flows through the piping system,some of the potential energy is lost due to friction.
hƒ=4ƒLv²/2gD
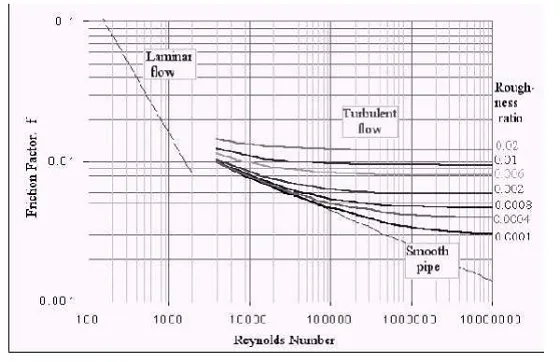
MOODY’S DIAGRAM
Moody’s diagram is plotted between various values of friction factor(ƒ),Reynolds
number(Re) and relative roughness(R/K) as shown in figure 2.6.For any turbulent flowproblem,the values of friction factor(ƒ) can therefore be determined from Moody’s diagram,if the numerical values of R/K for the pipe and Rе of flow are known.
The Moody’s diagram has plotted from the equation
1/√ ƒ-2.0 log10(R/K)=1.74-2.0 log10[1+18.7/(R/K/Re/ ƒ)]
Where,R/K=relative roughness
ƒ=friction factor and Re=Reynolds number.

CLASSIFICATION OF BOUNDARY LAYER THICKNESS
1. Displacements thickness(δ*)
2. Momentum thickness(θ)
3. Energy thickness(δe)
BOUNDARY LAYER SEPARATION
The boundary layer leaves the surface and gets separated from it. This phenomenon is known as boundary layer separation.
LOSSESS IN PIPES
When a fluid flowing through a pipe, certain resistance is offered to the flowing fluid, it results in causing a loss of energy.
The loss is classified as:
1. Major losses
2. Minor losses
Major Losses in Pipe Flow
The major loss of energy is caused by friction in pipe. It may be computed by Darcy-weisbach equation.
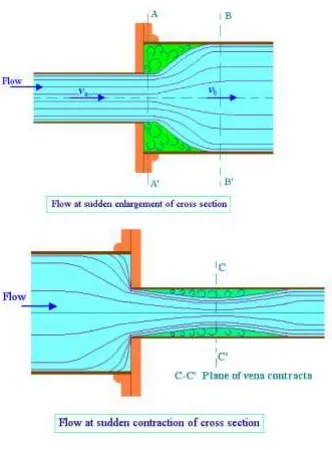
Minor Losses in Pipe Flow
The loss of energy caused on account of the change in velocity of flowing fluid is called minor loss of energy.
FLOW THOUGH PIPES IN SERIES AND PARALLEL
Pipes in Series
The pipes of different diamers and lengths which are connected with one another to form a single pipeline.
Pipes in Parallel
When a main pipeline divides into two or more parallel pipes which again join together to form a single pipe and continuous as a main line
GLOSSARY
HGL –Hydraulic gradient line
TEL – Total energy line.