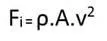
Reynolds Experiment
Reynolds number is the ratio of the inertial force of flowing fluid to the viscous force of the fluid. Inertial force of the fluid can be expressed as :
Inertial force, Fi = mass X acceleration
= (density X volume) X (Velocity / time)
= (density X Area) X (Velocity X Velocity)
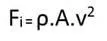
Viscous force, Fv = Shear stress X area
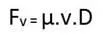
Therefore, Reynolds number is given by :
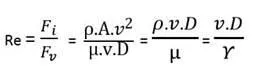
Where, v = velocity of fluid flow
D = diameter of glass tube


Fig 1: Reynolds Experiment Apparatus
Test Procedure of Reynolds experiment is as follows:
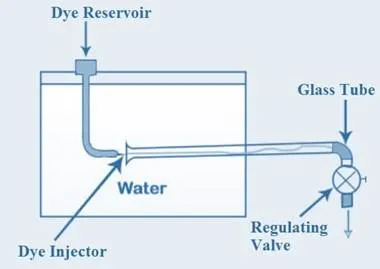
Fig 2: Reynolds Apparatus Working Condition
Following observations should be made while passing colored fluid through glass tube.
Check the formation or appearance of dye filament in the glass tube for different velocities and note down the flow type based on its appearance from below three cases.
Case 1: If dye filament forms straight line, then it is called as laminar flow.
Case 2: If dye filament flows in a slightly wavy manner, then it is said to be transition flow.
Case 3: If dye filament diffuses over the entire cross section of tube while passing, then it is called as turbulent flow. All of these three flows are represented in below figure.

Fig 3: Types of Flows in Pipe Flow
Diameter of glass tube, D =
Measuring tank dimensions (breadth and width) =
Table 1: Reynolds Experiment Observations
S.no | Observed Flow type | Time (t) (seconds) | V, Volume of Water collected in t seconds ( m3 ) | Discharge (Q) | Velocity, v | Reynolds Number, Re |
1 | Laminar |
|
|
|
|
|
2 | Transition |
|
|
|
|
|
3 | Turbulent |
|
|
|
|
|
Volume of water collected in tank in t seconds, V = area of tank X Rise of water level in t seconds
Discharge, Q = Volume / time
Velocity of flow, v = Discharge / area of glass tube
Reynolds number, Re =
Reynolds number of flow =