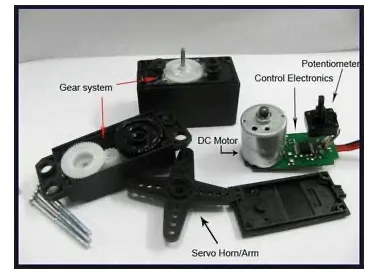
What is a Servomotor?

A servomotor is a linear actuator or rotary actuator that allows for precise control of linear or angular position, acceleration, and velocity. It consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servomotors.
There are some special types of applications of an electric motor where the rotation of the motor is required for just a certain angle. For these applications, we require some special types of motor with some special arrangement which makes the motor rotate a certain angle for a given electrical input (signal). For this purpose, servo motor comes into the picture.
The servo motor is usually a simple DC motor controlled for specific angular rotation with the help of additional servomechanism (a typical closed-loop feedback control system). Nowadays, servo systems are used widely in industrial applications.
Servo motor applications are also commonly seen in remote-controlled toy cars for controlling the direction of motion, and it is also very widely used as the motor which moves the tray of a CD or DVD player. Besides these, there are hundreds of servo motor applications we see in our daily life.
The main reason behind using a servo is that it provides angular precision, i.e. it will only rotate as much we want and then stop and wait for the next signal to take further action. The servo motor is unlike a standard electric motor which starts turning as when we apply power to it, and the rotation continues until we switch off the power. We cannot control the rotational progress of electrical motor, but we can only control the speed of rotation and can turn it ON and OFF. Small servo motors are included many beginner Arduino starter kits, as they are easy to operate as part of a small electronics projects.