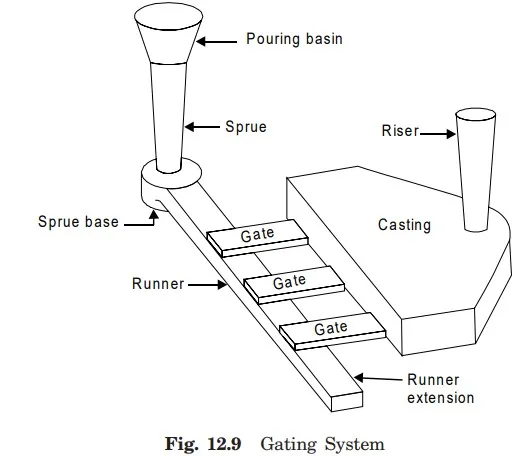
GATING SYSTEM IN MOLD

1. Pouring basin
It is the conical hollow element or tapered hollow vertical portion of the gating system which helps to feed the molten metal initially through the path of gating system to mold cavity. It may be made out of core sand or it may be cut in cope portion of the sand mold. It makes easier for the ladle operator to direct the flow of molten metal from crucible to pouring basin and sprue. It helps in maintaining the required rate of liquid metal flow. It reduces turbulence and vertexing at the sprue entrance. It also helps in separating dross, slag and foreign element etc. from molten metal before it enters the sprue.
2. Sprue
It is a vertical passage made generally in the cope using tapered sprue pin. It is connected at bottom of pouring basin. It is tapered with its bigger end at to receive the molten metal the smaller end is connected to the runner. It helps to feed molten metal without turbulence to the runner which in turn reaches the mold cavity through gate. It some times possesses skim bob at its lower end. The main purpose of skim bob is to collect impurities from molten metal and it does not allow them to reach the mold cavity through runner and gate.
3. Gate
It is a small passage or channel being cut by gate cutter which connect runner with the mould cavity and through which molten metal flows to fill the mould cavity. It feeds the liquid metal to the casting at the rate consistent with the rate of solidification.
4. Choke
It is that part of the gating system which possesses smallest cross-section area. In choked system, gate serves as a choke, but in free gating system sprue serves as a choke.
5. Runner
It is a channel which connects the sprue to the gate for avoiding turbulence and gas entrapment.
6. Riser
It is a passage in molding sand made in the cope portion of the mold. Molten metal rises in it after filling the mould cavity completely. The molten metal in the riser compensates the shrinkage during solidification of the casting thus avoiding the shrinkage defect in the casting. It also permits the escape of air and mould gases. It promotes directional solidification too and helps in bringing the soundness in the casting.
7. Chaplets
Chaplets are metal distance pieces inserted in a mould either to prevent shifting of mould or locate core surfaces. The distances pieces in form of chaplets are made of parent metal of which the casting is. These are placed in mould cavity suitably which positions core and to give extra support to core and mould surfaces. Its main objective is to impart good alignment of mould and core surfaces and to achieve directional solidification. When the molten metal is poured in the mould cavity, the chaplet melts and fuses itself along with molten metal during solidification and thus forms a part of the cast material. Various types of chaplets are shown in Fig. 12.10. The use of the chaplets is depicted in Fig. 12.11.

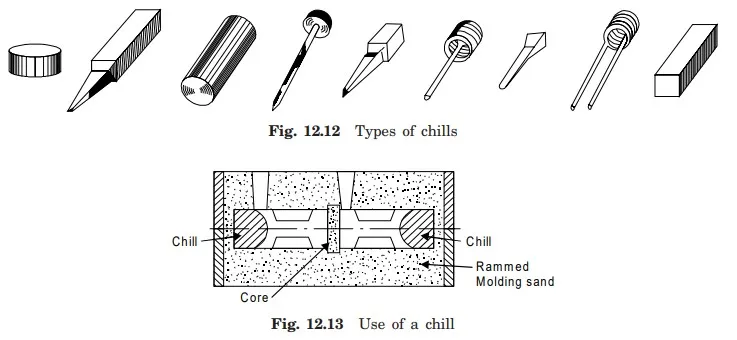
8. Chills
In some casting, it is required to produce a hard surface at a particular place in the casting. At that particular position, the special mould surface for fast extraction of heat is to be made. The fast heat extracting metallic materials known as chills will be incorporated separately along with sand mould surface during molding. After pouring of molten metal and during solidification, the molten metal solidifies quickly on the metallic mould surface in comparison to other mold sand surfaces. This imparts hardness to that particular surface because of this special hardening treatment through fast extracting heat from that particular portion. Thus, the main function of chill is to provide a hard surface at a localized place in the casting by way of special and fast solidification. Various types of chills used in some casting processes are shown in Fig. 12.12. The use of a chill in the mold is depicted in Fig. 12.13.